The salivary alpha-amylase concentration in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A case-control study
- PMID: 37180687
- PMCID: PMC10166745
The salivary alpha-amylase concentration in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A case-control study
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is one of the most common chronic inflammatory diseases. Previous studies have reported an association between stress and salivary alpha-amylase. The aim of this study was to investigate the concentration of salivary alpha-amylase in patients with RA (by elimination of stress factor).
Materials and methods: In this case-control study, we enrolled 50 patients with RA and 48 healthy patients as the control group. The perceived stress scale questionnaire was used to evaluate scores of stress in both case and control groups, and then the participants with high scores of stress were excluded from the study. Moreover, the alpha-amylase activity kit was used for the assessment of the levels of salivary alpha-amylase. In all analyses, the significance level was considered to be < 0.05. Finally, the obtained data were analyzed by SPSS22.
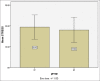
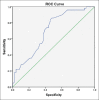
Results: Our results indicated a high score of stress in the case group (19.42 ± 5.83 units) compared with the control group (18.02 ± 6.07 units) which was not statistically significant (P < 0.248). Moreover, we demonstrated a high salivary alpha-amylase concentration in the case group (340.65 ± 38.04 units) compared to the control group (302.62 ± 58.72 units), which was statistically significant (P < 0.001). The sensitivity and specificity of this method, at >312 alpha-amylase concentrations, were 80% and 46%, respectively.
Conclusion: In general, we indicated that the alpha-amylase concentration in patients with RA is higher than the healthy controls, and can be used as a codiagnostic factor.
Keywords: Rheumatoid arthritis; salivary alpha-amylases; stress disorder.
Copyright: © 2023 Dental Research Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare that they have no conflicts of interest, real or perceived, financial or nonfinancial in this article.
Figures

References
-
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2016;388:2023–38. - PubMed
-
- Hoxha M. A systematic review on the role of eicosanoid pathways in rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Med Sci. 2018;63:22–9. - PubMed
-
- Wasserman AM. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84:1245–52. - PubMed
-
- Atzeni F, Talotta R, Masala IF, Bongiovanni S, Boccassini L, Sarzi-Puttini P. Biomarkers in rheumatoid arthritis. Isr Med Assoc J. 2017;19:512–6. - PubMed
-
- Kunikullaya UK, Kumar MA, Ananthakrishnan V, Jaisri G. Stress as a cause of recurrent aphthous stomatitis and its correlation with salivary stress markers. Chin J Physiol. 2017;60:226–30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
