Development of liposomal contrast agent with high iodine concentration and minimal effect on renal function
- PMID: 37180756
- PMCID: PMC10172707
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2023.101473
Development of liposomal contrast agent with high iodine concentration and minimal effect on renal function
Abstract
Purpose: The use of contrast media is essential to achieve high accuracy in diagnostic imaging. Iodine contrast media, one of these contrast media, has nephrotoxicity as a side effect. Therefore, the development of iodine contrast media that can reduce nephrotoxicity is expected. Since liposomes are generally adjustable in size (100-300 nm) and are not filtered by the renal glomerulus, we hypothesized that iodine contrast media could be encapsulated in liposomes and administered to avoid the nephrotoxicity of iodine contrast media. The aim of this study is to develop an iomeprol-containing liposome (IPL) agent with high iodine concentration and to investigate the effect of intravenous administration of IPL on renal function in a rat model with chronic kidney injury.
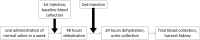
Materials and methods: IPLs were prepared by encapsulating an iomeprol (400mgI/mL) solution in liposomes by a kneading method using a rotation-revolution mixer. Radiodensities of iomeprol and IPL were measured. IPL or iopamidol at normal dose (0.74 g I/kg) or high dose (3.7 g I/kg) was administered to healthy and 5/6-nephrectomized rats (n = 3-6). Serum creatinine (sCr) and histopathological change of tubular epithelial cells were evaluated after injection.
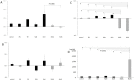
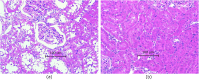
Results: The iodine concentration of IPL was 220.7 mgI/mL, equivalent to 55.2% of the iodine concentration of iomeprol. The CT values of IPL was 4731.6 ± 53.2 HU, 59.04% that of iomeprol. The ratios of change in sCr in 5/6-nephrectomized rats that received high-dose iopamidol were 0.73, which were significantly higher than that in 5/6-nephrectomized rats that received high-dose IPL (-0.03) (p = 0.006). Change in foamy degeneration of tubular epithelial cells was confirmed in 5/6-nephrectomized rats that received high-dose iopamidol than that in the sham control group and healthy rats that received normal dose iopamiron (p = 0.016, p = 0.032, respectively). Foamy degeneration of tubular epitherial cells was rarely observed in the IPL injection group.
Conclusions: We developed new liposomal contrast agents that have high iodine concentration and minimal effect on renal function.
Keywords: Contrast-induced acute kidney injury; Iodinated contrast agent; Liposomal contrast agent; Liposome; Nephrotoxicity.
© 2023 The Authors.
Figures

References
-
- Giardino Angela, Gupta Supriya, Olson Emmi, Sepulveda Karla, Leon Lenchik, Jana Ivanidze, Rakow-Penner Rebecca, Patel Midhir J., Subramania Rathan M., Ganeshan Dhakshinamoorthy. Role of imaging in the era of precision medicine. Acad. Radiol. 2017 May;24(5):639–649. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2016.11.021. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Taiji Ryosuke, Nishiofuku Hideyuki, Tanaka Toshihiro, Minamiguchi Kiyoyuki, Fukuoka Yasushi, Saito Natsuhiko, Taguchi Hidehiko, Matsumoto Takeshi, Marugami Nagaaki, Hira Toshiko, Kichikawa Kimihiko. Useful parameters in dynamic contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for identifying early response to chemotherapy in a rat liver tumor model. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2021;15(11):15. doi: 10.25259/JCIS_6_2020.eCollection2021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ochi Tomoko, Taoka Toshiaki, Matsuda Ryosuke, Sakamoto Masahiko, Akashi Toshiaki, Tamamoto Tetsuro, Sugimoto Tadashi, Sakaguchi Hiroshi, Hasegawa Masatoshi, Nakase Hiroyuki, kichikawa Kimihiko. Comparison between two separate injections and a single injection of double-dose contrast medium for contrast-enhanced MR imaging of metastatic brain tumors. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2014;13(4):221–229. doi: 10.2463/mrms.2013-0068. Epub 2014 Aug 27. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liu Tong-qiang, Luo Wei-li, Tan Xiao, Fang Yi, Chen Jing, Zhang Hui, Yu Xiao-fang, Cai Jie-ru, Ding Xiao-qiang. A novel contrast-induced acute kidney injury model based on the 5/6-nephrectomy rat and nephrotoxicological evaluation of iohexol and iodixanol in vivo. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014;2014 doi: 10.1155/2014/427560. Epub 2014 Nov 11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

