Electroreduction of CO2 in a Non-aqueous Electrolyte-The Generic Role of Acetonitrile
- PMID: 37180961
- PMCID: PMC10167651
- DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.3c00236
Electroreduction of CO2 in a Non-aqueous Electrolyte-The Generic Role of Acetonitrile
Abstract
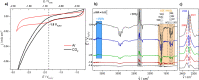
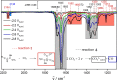
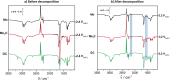
Transition metal carbides, especially Mo2C, are praised to be efficient electrocatalysts to reduce CO2 to valuable hydrocarbons. However, on Mo2C in an aqueous electrolyte, exclusively the competing hydrogen evolution reaction takes place, and this discrepancy to theory was traced back to the formation of a thin oxide layer at the electrode surface. Here, we study the CO2 reduction activity at Mo2C in a non-aqueous electrolyte to avoid such passivation and to determine products and the CO2 reduction reaction pathway. We find a tendency of CO2 to reduce to carbon monoxide. This process is inevitably coupled with the decomposition of acetonitrile to a 3-aminocrotonitrile anion. Furthermore, a unique behavior of the non-aqueous acetonitrile electrolyte is found, where the electrolyte, instead of the electrocatalyst, governs the catalytic selectivity of the CO2 reduction. This is evidenced by in situ electrochemical infrared spectroscopy on different electrocatalysts as well as by density functional theory calculations.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Global Monitoring Laboratory . Carbon Cycle Greenhouse Gases, 2022. Available at https://gml.noaa.gov/ccgg/trends/ (accessed Nov 15, 2022).
-
- SAWYER J. S. Man-made Carbon Dioxide and the “Greenhouse” Effect. Nature 1972, 239, 23–26. 10.1038/239023a0. - DOI
-
- Khezri B.; Fisher A. C.; Pumera M. CO2 reduction: the quest for electrocatalytic materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 8230–8246. 10.1039/C6TA09875D. - DOI
-
- Nitopi S.; Bertheussen E.; Scott S. B.; Liu X.; Engstfeld A. K.; Horch S.; Seger B.; Stephens I. E. L.; Chan K.; Hahn C.; Nørskov J. K.; Jaramillo T. F.; Chorkendorff I. Progress and Perspectives of Electrochemical CO2 Reduction on Copper in Aqueous Electrolyte. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 7610–7672. 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00705. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
