First gene-edited calf with reduced susceptibility to a major viral pathogen
- PMID: 37181049
- PMCID: PMC10167990
- DOI: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad125
First gene-edited calf with reduced susceptibility to a major viral pathogen
Abstract
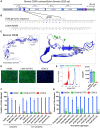
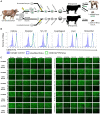
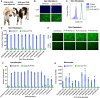
Bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) is one of the most important viruses affecting the health and well-being of bovine species throughout the world. Here, we used CRISPR-mediated homology-directed repair and somatic cell nuclear transfer to produce a live calf with a six amino acid substitution in the BVDV binding domain of bovine CD46. The result was a gene-edited calf with dramatically reduced susceptibility to infection as measured by reduced clinical signs and the lack of viral infection in white blood cells. The edited calf has no off-target edits and appears normal and healthy at 20 months of age without obvious adverse effects from the on-target edit. This precision bred, proof-of-concept animal provides the first evidence that intentional genome alterations in the CD46 gene may reduce the burden of BVDV-associated diseases in cattle and is consistent with our stepwise, in vitro and ex vivo experiments with cell lines and matched fetal clones.
Keywords: BVDV; CD46; CRISPR; bovine viral diarrhea virus; gene editing.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of National Academy of Sciences 2023.
Figures

References
-
- Baker JC. 1995. The clinical manifestations of bovine viral diarrhea infection. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 11:425–445. - PubMed
-
- Bolin SR. 2002. Bovine viral diarrhea virus in mixed infections. In: Brogden KA, Guthmiller JM, editors. Polymicrobial diseases. Washington (DC): ASM Press. - PubMed
-
- Bruschke CJ, Weerdmeester K, Van Oirschot JT, Van Rijn PA. 1998. Distribution of bovine virus diarrhoea virus in tissues and white blood cells of cattle during acute infection. Vet Microbiol. 64:23–32. - PubMed
-
- Liess B, Moennig V, Pohlenz J, Trautwein G. 2012. Ruminant pestivirus infections: virology, pathogenesis, and perspectives of prophylaxis. Berlin (Germany): Springer Science & Business Media.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

