The image and data archive at the laboratory of neuro imaging
- PMID: 37181736
- PMCID: PMC10169596
- DOI: 10.3389/fninf.2023.1173623
The image and data archive at the laboratory of neuro imaging
Abstract
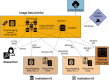
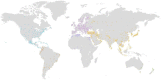
The Image and Data Archive (IDA) is a secure online resource for archiving, exploring, and sharing neuroscience data run by the Laboratory of Neuro Imaging (LONI). The laboratory first started managing neuroimaging data for multi-centered research studies in the late 1990's and since has become a nexus for many multi-site collaborations. By providing management and informatics tools and resources for de-identifying, integrating, searching, visualizing, and sharing a diverse range of neuroscience data, study investigators maintain complete control over data stored in the IDA while benefiting from a robust and reliable infrastructure that protects and preserves research data to maximize data collection investment.
Keywords: IDA; data archive; data repository; data sharing; neuroimaging.
Copyright © 2023 Neu, Crawford and Toga.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

