Complete Regression of an 8-cm Desmoid Fibromatosis After Treatment With Tamoxifen
- PMID: 37182013
- PMCID: PMC10173676
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.37431
Complete Regression of an 8-cm Desmoid Fibromatosis After Treatment With Tamoxifen
Abstract
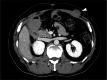
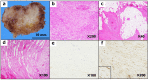
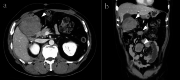
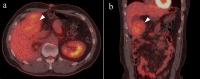
We report a case of a relatively large desmoid fibromatosis that responded completely to tamoxifen as a single drug therapy. A 47-year-old Japanese man underwent laparoscopy-assisted endoscopic submucosal dissection for a duodenal polyp. He developed postoperative generalized peritonitis and underwent an emergency laparotomy. Sixteen months after the surgery, a subcutaneous mass was found on the abdominal wall. Biopsy of the mass revealed estrogen receptor alpha-negative desmoid fibromatosis. The patient underwent total tumor resection. Two years after the initial surgery, he was found to have multiple intra-abdominal masses, with the largest mass measuring 8 cm in diameter. Biopsy revealed fibromatosis, as in the case of the subcutaneous mass. Complete resection was impossible due to the proximity of the duodenum and superior mesenteric artery. Tamoxifen was administered for three years, resulting in complete regression of the masses. No recurrence was observed for the following three years. This case indicates that relatively large desmoid fibromatosis can be successfully treated with a selective estrogen receptor modulator alone and that its effect is not dependent on the estrogen receptor alpha status of the tumor.
Keywords: desmoid fibromatosis; estrogen receptor; gastroenterological surgery; selective estrogen receptor modulator; tamoxifen.
Copyright © 2023, Suzuki et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Desmoid fibromatosis: management in an era of increasing options. Ratan R, Roland CL, Bishop AJ. Curr Oncol Rep. 2021;23:41. - PubMed
-
- Prognostic factors influencing progression-free survival determined from a series of sporadic desmoid tumors: a wait-and-see policy according to tumor presentation. Salas S, Dufresne A, Bui B, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:3553–3558. - PubMed
-
- An update on the management of sporadic desmoid-type fibromatosis: a European Consensus Initiative between Sarcoma PAtients EuroNet (SPAEN) and European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC)/Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group (STBSG) Kasper B, Baumgarten C, Garcia J, et al. Ann Oncol. 2017;28:2399–2408. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anti-oestrogen therapy in the treatment of desmoid tumours: a systematic review. Bocale D, Rotelli MT, Cavallini A, Altomare DF. Colorectal Dis. 2011;13:0–95. - PubMed
-
- Long-term outcome of sporadic and FAP-associated desmoid tumors treated with high-dose selective estrogen receptor modulators and sulindac: a single-center long-term observational study in 134 patients. Quast DR, Schneider R, Burdzik E, Hoppe S, Möslein G. Fam Cancer. 2016;15:31–40. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
