Should We Use bDMARDs as an Induction Therapy in Early and Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis? Results at 5 years from the ERA UCLouvain Brussels Cohort
- PMID: 37183237
- PMCID: PMC10326217
- DOI: 10.1007/s40744-023-00551-3
Should We Use bDMARDs as an Induction Therapy in Early and Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis? Results at 5 years from the ERA UCLouvain Brussels Cohort
Abstract
Introduction: This study sought to analyze the benefit of an early induction therapy with a biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARD) during the first year of treatment with a 5-year follow-up in early rheumatoid arthritis (ERA).
Methods: We included ERA patients from the UCLouvain Brussels cohort who met the American College of Rheumatology (ACR)/European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 2010 classification criteria and were naïve to DMARDs. ERA patients were divided into two groups according to whether they received an induction bDMARD therapy or a standard therapy with methotrexate (MTX). Clinical response after the induction treatment at 6 and 12 months followed by a MTX maintenance therapy at 36 and 60 months was evaluated.
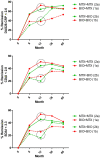
Results: Data from 470 ERA patients were collected, 189 received a bDMARD and 281 initiated MTX alone. In the bDMARD group, disease activity and HAQ were higher at baseline. A total of 391 patients were followed up to 5 years. We then divided each group into two subgroups according to the last treatment they received at 5 years: bDMARD > MTX (n = 95), bDMARD > bDMARD (n = 59); MTX > MTX (n = 134), MTX > bDMARD (n = 103). During the induction, we observed a clinical response with a large number of patients achieving DAS28-CRP remission. According to a treat-to-target (T2T) approach, remission rate was stable on MTX monotherapy or rescued by the addition or prolongation of a bDMARD. Interestingly, bDMARD followed by a MTX maintenance therapy experienced a stable and sustained DAS28-CRP remission rate in 53% of the ERA patients at year 5.
Conclusions: Long-term remission is an achievable goal in ERA. Our results suggest that a bDMARD induction therapy followed by MTX maintenance therapy could be an interesting option.
Keywords: Biological versus conventional synthetic DMARDs; Early arthritis; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Emilie Sapart, Tatiana Sokolova, Stéphanie de Montjoye, Stéphanie Dierckx, Adrien Nzeusseu, Aleksandra Avramovska, Laurent Meric de Bellefon and Patrick Durez have nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tofacitinib for Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis After the Failure of Disease-Modifying Anti-rheumatic Drugs: An Evidence Review Group Perspective of a NICE Single Technology Appraisal.Pharmacoeconomics. 2018 Sep;36(9):1063-1072. doi: 10.1007/s40273-018-0639-0. Pharmacoeconomics. 2018. PMID: 29546668 Review.
-
The effect of deep or sustained remission on maintenance of remission after dose reduction or withdrawal of etanercept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 Jul 5;21(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s13075-019-1937-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31277720 Free PMC article.
-
Assessments of the unmet need in the management of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: analyses from the NOR-DMARD registry.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019 Mar 1;58(3):481-491. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key338. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019. PMID: 30508189 Free PMC article.
-
Tapering of biological antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis patients is achievable and cost-effective in daily clinical practice: data from the Brussels UCLouvain RA Cohort.Arthritis Res Ther. 2020 Apr 28;22(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02165-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32345367 Free PMC article.
-
Combination therapy with biologic agents in rheumatic diseases: current and future prospects.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2016 Oct;8(5):192-202. doi: 10.1177/1759720X16665330. Epub 2016 Aug 29. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2016. PMID: 27721905 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous