Transcriptomic analysis reveals the role of SIX1 in mouse cranial neural crest patterning and bone development
- PMID: 37183792
- PMCID: PMC10592572
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.597
Transcriptomic analysis reveals the role of SIX1 in mouse cranial neural crest patterning and bone development
Abstract
Background: Genetic variants of the transcription factor SIX1 and its co-factor EYA1 underlie 50% of Branchio-oto-renal syndrome (BOR) cases. BOR is characterized by craniofacial defects, including malformed middle ear ossicles leading to conductive hearing loss. In this work, we expand our knowledge of the Six1 gene regulatory network by using a Six1-null mouse line to assess gene expression profiles of E10.5 mandibular arches, which give rise to the neural crest (NC)-derived middle ear ossicles and lower jaw, via bulk RNA sequencing.
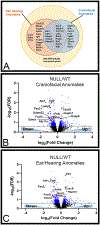
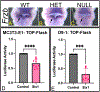
Results: Our transcriptomic analysis led to the identification of 808 differentially expressed genes that are related to translation, NC cell differentiation, osteogenesis, and chondrogenesis including components of the WNT signaling pathway. As WNT signaling is a known contributor to bone development, we demonstrated that SIX1 is required for expression of the WNT antagonist Frzb in the mandibular arch, and determined that SIX1 expression results in repression of WNT signaling.
Conclusion: Our results clarify the mechanisms by which SIX1 regulates the development of NC-derived craniofacial elements that are altered in SIX1-associated disorders. In addition, this work identifies novel genes that could be causative to this birth defect and establishes a link between SIX1 and WNT signaling during patterning of NC cells.
Keywords: Branchio-oto-renal syndrome; SIX1; craniofacial defects; hearing loss; transcriptional regulation.
© 2023 American Association for Anatomy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mcrs1 interacts with Six1 to influence early craniofacial and otic development.Dev Biol. 2020 Nov 1;467(1-2):39-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2020.08.013. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32891623 Free PMC article.
-
Sobp modulates the transcriptional activation of Six1 target genes and is required during craniofacial development.Development. 2021 Sep 1;148(17):dev199684. doi: 10.1242/dev.199684. Epub 2021 Sep 6. Development. 2021. PMID: 34414417 Free PMC article.
-
Six1 proteins with human branchio-oto-renal mutations differentially affect cranial gene expression and otic development.Dis Model Mech. 2020 Mar 3;13(3):dmm043489. doi: 10.1242/dmm.043489. Dis Model Mech. 2020. PMID: 31980437 Free PMC article.
-
Branchio-oto-renal syndrome.Am J Med Genet A. 2007 Jul 15;143A(14):1671-8. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.31561. Am J Med Genet A. 2007. PMID: 17238186 Review.
-
Contribution of cranial neural crest cells to mouse skull development.Int J Dev Biol. 2017;61(8-9):495-503. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.170051gc. Int J Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 29139535 Review.
Cited by
-
Spatiotemporal Molecular Architecture of Lineage Allocation and Cellular Organization in Tooth Morphogenesis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Dec;11(47):e2403627. doi: 10.1002/advs.202403627. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39535354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chai Y, Jiang X, Ito Y, et al. Fate of the mammalian cranial neural crest during tooth and mandibular morphogenesis. Development. Apr 2000;127(8):1671–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

