Advanced Urea Precursors Driven NiCo2O4 Nanostructures Based Non-Enzymatic Urea Sensor for Milk and Urine Real Sample Applications
- PMID: 37185519
- PMCID: PMC10135918
- DOI: 10.3390/bios13040444
Advanced Urea Precursors Driven NiCo2O4 Nanostructures Based Non-Enzymatic Urea Sensor for Milk and Urine Real Sample Applications
Abstract
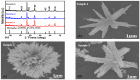
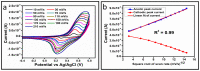
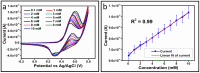
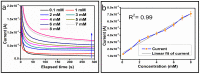
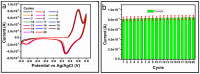
The electrochemical performance of NiCo2O4 with urea precursors was evaluated in order to develop a non-enzymatic urea sensor. In this study, NiCo2O4 nanostructures were synthesized hydrothermally at different concentrations of urea and characterized using scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. Nanostructures of NiCo2O4 exhibit a nanorod-like morphology and a cubic phase crystal structure. Urea can be detected with high sensitivity through NiCo2O4 nanostructures driven by urea precursors under alkaline conditions. A low limit of detection of 0.05 and an analytical range of 0.1 mM to 10 mM urea are provided. The concentration of 006 mM was determined by cyclic voltammetry. Chronoamperometry was used to determine the linear range in the range of 0.1 mM to 8 mM. Several analytical parameters were assessed, including selectivity, stability, and repeatability. NiCo2O4 nanostructures can also be used to detect urea in various biological samples in a practical manner.
Keywords: NiCo2O4 nanostructures; alkaline conditions; non-enzymatic sensor; urea precursors.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no competing interest in the presented research.
Figures



References
-
- Roy B., Brahma B., Ghosh S., Pankaj P., Mandal G. Evaluation of milk urea concentration as useful indicator for dairy herd management: A review. Asian J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2011;6:1–19. doi: 10.3923/ajava.2011.1.19. - DOI
-
- Francis P.S., Lewis S.W., Lim K.F. Analytical methodology for the determination of urea: Current practice and future trends. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2002;21:389–400. doi: 10.1016/S0165-9936(02)00507-1. - DOI
-
- Bisht V., Takashima W., Kaneto K. An amperometric urea biosensor based on covalent immobilization of urease onto an electrochemically prepared copolymer poly (N-3-aminopropyl pyrrole-co-pyrrole) film. Biomaterials. 2005;26:3683–3690. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

