DNA Nanotechnology for Investigating Mechanical Signaling in the Immune System
- PMID: 37186502
- PMCID: PMC11336604
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202302967
DNA Nanotechnology for Investigating Mechanical Signaling in the Immune System
Abstract
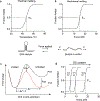
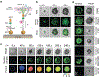
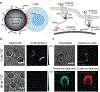
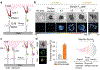
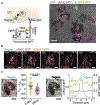
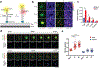
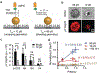
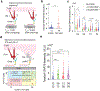
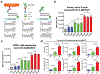
Immune recognition occurs at specialized cell-cell junctions when immune cells and target cells physically touch. In this junction, groups of receptor-ligand complexes assemble and experience molecular forces that are ultimately generated by the cellular cytoskeleton. These forces are in the range of piconewton (pN) but play crucial roles in immune cell activation and subsequent effector responses. In this minireview, we will review the development of DNA based molecular tension sensors and their applications in mapping and quantifying mechanical forces experienced by immunoreceptors including T-cell receptor (TCR), Lymphocyte function-associated antigen (LFA-1), and the B-cell receptor (BCR) among others. In addition, we will highlight the use of DNA as a mechanical gate to manipulate mechanotransduction and decipher how mechanical forces regulate antigen discrimination and receptor signaling.
Keywords: DNA Tension Probe; Force Manipulating; Force Sensing; Immunoreceptor; Mechanical Signalling.
© 2023 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Figures
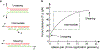
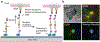
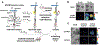
Similar articles
-
DNA-based nanoparticle tension sensors reveal that T-cell receptors transmit defined pN forces to their antigens for enhanced fidelity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 May 17;113(20):5610-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1600163113. Epub 2016 May 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27140637 Free PMC article.
-
Ratiometric Tension Probes for Mapping Receptor Forces and Clustering at Intermembrane Junctions.Nano Lett. 2016 Jul 13;16(7):4552-9. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b01817. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Nano Lett. 2016. PMID: 27192323 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying T cell receptor mechanics at membrane junctions using DNA origami tension sensors.Nat Nanotechnol. 2024 Nov;19(11):1674-1685. doi: 10.1038/s41565-024-01723-0. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Nat Nanotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39103452
-
Molecular Tension Probes for Imaging Forces at the Cell Surface.Acc Chem Res. 2017 Dec 19;50(12):2915-2924. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00305. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Acc Chem Res. 2017. PMID: 29160067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating piconewton forces in cells by FRET-based molecular force microscopy.J Struct Biol. 2017 Jan;197(1):37-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2016.03.011. Epub 2016 Mar 12. J Struct Biol. 2017. PMID: 26980477 Review.
Cited by
-
Force-Induced Site-Specific Enzymatic Cleavage Probes Reveal That Serial Mechanical Engagement Boosts T Cell Activation.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 Mar 20;146(11):7233-7242. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c08137. Epub 2024 Mar 7. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 38451498 Free PMC article.
-
Reversible strain-promoted DNA polymerization.Sci Adv. 2024 Apr 26;10(17):eado8020. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ado8020. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38657068 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring Integrin Force Loading Rates Using a Two-Step DNA Tension Sensor.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 Aug 21;146(33):23034-23043. doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c03629. Epub 2024 Aug 12. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 39133202 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoscale Cellular Traction Force Quantification: CRISPR-Cas12a Supercharged DNA Tension Sensors in Nanoclustered Ligand Patterns.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 Feb 5;17(5):7339-7352. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c18358. Epub 2025 Jan 27. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 39868861 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid nanoparticle-mediated RNA delivery for immune cell modulation.Eur J Immunol. 2024 Dec;54(12):e2451008. doi: 10.1002/eji.202451008. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Eur J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39279550 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Huppa JB, Davis MM, Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 973–983. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman BD, Grashoff C, Schwartz MA, Nature 2011, 475, 316–323; - PMC - PubMed
- Vining KH, Mooney DJ, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 728–742; - PMC - PubMed
- Trepat X, Wasserman MR, Angelini TE, Millet E, Weitz DA, Butler JP, Fredberg JJ, Nat. Phys. 2009, 5, 426–430;
- Huse M, Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 679–690. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Das DK, Feng Y, Mallis RJ, Li X, Keskin DB, Hussey RE, Brady SK, Wang JH, Wagner G, Reinherz EL, Lang MJ, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2015, 112, 1517–1522; - PMC - PubMed
- Kim ST, Takeuchi K, Sun ZY, Touma M, Castro CE, Fahmy A, Lang MJ, Wagner G, Reinherz EL, J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 31028–31037. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gaud G, Lesourne R, Love PE, Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 485–497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

