Influence of well-being and quality of work-life on quality of care among healthcare professionals in southwest, Nigeria
- PMID: 37188741
- PMCID: PMC10185691
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-25057-w
Influence of well-being and quality of work-life on quality of care among healthcare professionals in southwest, Nigeria
Abstract
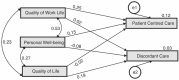
The Nigerian healthcare industry is bedevilled with infrastructural dilapidations and a dysfunctional healthcare system. This study investigated the influence of healthcare professionals' well-being and quality of work-life (QoWL) on the quality of care (QoC) of patients in Nigeria. A multicentre cross-sectional study was conducted at four tertiary healthcare institutions in southwest, Nigeria. Participants' demographic information, well-being, quality of life (QoL), QoWL, and QoC were obtained using four standardised questionnaires. Data were summarised using descriptive statistics. Inferential statistics included Chi-square, Pearson's correlation, independent samples t-test, confirmatory factor analyses and structural equation model. Medical practitioners (n = 609) and nurses (n = 570) constituted 74.6% of all the healthcare professionals with physiotherapists, pharmacists, and medical laboratory scientists constituting 25.4%. The mean (SD) participants' well-being = 71.65% (14.65), QoL = 61.8% (21.31), QoWL = 65.73% (10.52) and QoC = 70.14% (12.77). Participants' QoL had a significant negative correlation with QoC while well-being and quality of work-life had a significant positive correlation with QoC. We concluded that healthcare professionals' well-being and QoWL are important factors that influence the QoC rendered to patients. Healthcare policymakers in Nigeria should ensure improved work-related factors and the well-being of healthcare professionals to ensure good QoC for patients.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
ACO, NAO, OOO, MOO and CEM are staff or consultants to the institutions where the research was conducted. Other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organisation. Health workforce. https://www.who.int/health-topics/health-workforce#tab=tab_1 (Accessed 27 Oct 2022) (2022).
-
- World Health Organisation. Delivering quality health services: a global imperative for universal health coverage. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/272465/9789241513906-en... (Accessed 27 Oct 2022) (World Health Organisation, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, and The World Bank, 2018).
-
- Thakre SB, Thakre SS, Thakre SN. Quality of work life of nurses working at tertiary health care institution: A cross sectional study. Int. J. Community Med. Public Health. 2017;4:1627–1636. doi: 10.18203/2394-6040.ijcmph20171775. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

