Single-nucleus multi-omics of human stem cell-derived islets identifies deficiencies in lineage specification
- PMID: 37188763
- PMCID: PMC10264244
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-023-01150-8
Single-nucleus multi-omics of human stem cell-derived islets identifies deficiencies in lineage specification
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Single-nucleus multi-omics of human stem cell-derived islets identifies deficiencies in lineage specification.Nat Cell Biol. 2023 Oct;25(10):1546. doi: 10.1038/s41556-023-01219-4. Nat Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37558893 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
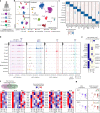
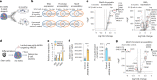
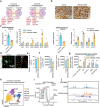
Insulin-producing β cells created from human pluripotent stem cells have potential as a therapy for insulin-dependent diabetes, but human pluripotent stem cell-derived islets (SC-islets) still differ from their in vivo counterparts. To better understand the state of cell types within SC-islets and identify lineage specification deficiencies, we used single-nucleus multi-omic sequencing to analyse chromatin accessibility and transcriptional profiles of SC-islets and primary human islets. Here we provide an analysis that enabled the derivation of gene lists and activity for identifying each SC-islet cell type compared with primary islets. Within SC-islets, we found that the difference between β cells and awry enterochromaffin-like cells is a gradient of cell states rather than a stark difference in identity. Furthermore, transplantation of SC-islets in vivo improved cellular identities overtime, while long-term in vitro culture did not. Collectively, our results highlight the importance of chromatin and transcriptional landscapes during islet cell specification and maturation.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
P.A., N.J.H., L.V.-C. and J. R. Millman are inventors on related patents and patent applications. J. R. Millman is/has served as a consultant/employee for Sana Biotechnology. L.V.-C. is currently employed by Sana Biotechnology. J. R. Millman and L.V.-C. have stock or stock options in Sana Biotechnology. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures













Comment in
-
Differences in stem cell-derived islets.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023 Aug;19(8):440. doi: 10.1038/s41574-023-00861-0. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37286797 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1TR002345/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 5-CDA-2017-391-A-N/JDRF/Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation/United States
- R01 DK127497/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM139774/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK114233/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007120/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA91842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK114233/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK127497/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM139774/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F31DK125068/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 3-APF-2020-930-A-N/JDRF/Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation/United States
- T32DK007120/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA091842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DK125068/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

