Predicting the Societal Value of Lecanemab in Early Alzheimer's Disease in Japan: A Patient-Level Simulation
- PMID: 37188886
- PMCID: PMC10310671
- DOI: 10.1007/s40120-023-00492-7
Predicting the Societal Value of Lecanemab in Early Alzheimer's Disease in Japan: A Patient-Level Simulation
Abstract
Introduction: Alzheimer's disease (AD), a neurodegenerative disorder that progresses from mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to dementia, is responsible for significant burden on caregivers and healthcare systems. In this study, data from the large phase III CLARITY AD trial were used to estimate the societal value of lecanemab plus standard of care (SoC) versus SoC alone against a range of willingness-to-pay (WTP) thresholds from a healthcare and societal perspective in Japan.
Methods: A disease simulation model was used to evaluate the impact of lecanemab on disease progression in early AD based on data from the phase III CLARITY AD trial and published literature. The model used a series of predictive risk equations based on clinical and biomarker data from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative and Assessment of Health Economics in Alzheimer's Disease II study. The model predicted key patient outcomes, including life years (LYs), quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), and total healthcare and informal costs of patients and caregivers.
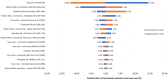
Results: Over a lifetime horizon, patients treated with lecanemab plus SoC gained an additional 0.73 LYs compared with SoC alone (8.50 years vs. 7.77 years). Lecanemab, with an average treatment duration of 3.68 years, was found to be associated with a 0.91 increase in patient QALYs and a total increase of 0.96 when accounting for caregiver utility. The estimated value of lecanemab varied according to the WTP thresholds (JPY 5-15 million per QALY gained) and the perspective employed. From the narrow healthcare payer's perspective, it ranged from JPY 1,331,305 to JPY 3,939,399. From the broader healthcare payer's perspective, it ranged from JPY 1,636,827 to JPY 4,249,702, while from the societal perspective, it ranged from JPY 1,938,740 to JPY 4,675,818.
Conclusion: The use of lecanemab plus SoC would improve health and humanistic outcomes with reduced economic burden for patients and caregivers with early AD in Japan.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; CLARITY AD; Cost-effectiveness; Economic burden; Japan; Lecanemab; Patient-level simulator; Quality-adjusted life years; Willingness-to-pay.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Ataru Igarashi received consultant fee from Eisai Co., Ltd. Mie Kasai Azuma and Kiyoyuki Tomita are employees of Eisai Co., Ltd. Quanwu Zhang is an employee of Eisai Inc. Weicheng Ye, Aditya Sardesai, Henri Folse, and Ameya Chavan are current employees of Evidera, a healthcare research firm that provides consulting and other research services to pharmaceutical, device, government, and non-government organizations. Eisai Inc. provided funding to Evidera for conducting the analysis and preparing the manuscript. Amir Abbas Tahami Monfared is an employee of Eisai Inc. He serves as Associate Editor for the
Figures

References
-
- Asada T. Prevalence of dementia and response to life dysfunction due to dementia in urban areas, Health Labour Sciences Research Grants, Dementia Countermeasures Comprehensive Research Project 2011-2012 Research Report. 2013.
-
- Prince MJ, Wimo A, Guerchet MM, Ali GC, Wu Y-T, Prina M. World Alzheimer Report 2015—the global impact of dementia: an analysis of prevalence, incidence, cost and trends. Alzheimer's Disease International, 2015. 84 p. https://www.alzint.org/u/WorldAlzheimerReport2015.pdf. Accessed 15 Mar 2023.
-
- World Health Organization. Dementia 2023. https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia. Accessed 20 Feb 2023.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

