Engineered allostery in light-regulated LOV-Turbo enables precise spatiotemporal control of proximity labeling in living cells
- PMID: 37188954
- PMCID: PMC10539039
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-023-01880-5
Engineered allostery in light-regulated LOV-Turbo enables precise spatiotemporal control of proximity labeling in living cells
Abstract
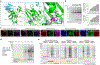
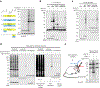
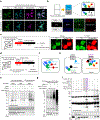
The incorporation of light-responsive domains into engineered proteins has enabled control of protein localization, interactions and function with light. We integrated optogenetic control into proximity labeling, a cornerstone technique for high-resolution proteomic mapping of organelles and interactomes in living cells. Through structure-guided screening and directed evolution, we installed the light-sensitive LOV domain into the proximity labeling enzyme TurboID to rapidly and reversibly control its labeling activity with low-power blue light. 'LOV-Turbo' works in multiple contexts and dramatically reduces background in biotin-rich environments such as neurons. We used LOV-Turbo for pulse-chase labeling to discover proteins that traffic between endoplasmic reticulum, nuclear and mitochondrial compartments under cellular stress. We also showed that instead of external light, LOV-Turbo can be activated by bioluminescence resonance energy transfer from luciferase, enabling interaction-dependent proximity labeling. Overall, LOV-Turbo increases the spatial and temporal precision of proximity labeling, expanding the scope of experimental questions that can be addressed with proximity labeling.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
S.-Y.L., J.S.C. and A.Y.T. have filed a patent application covering some aspects of this work (US Provisional Patent Application No. 63/488,940; CZ SF ref. CZB-273S-P1; Stanford ref. S22-487; KT ref. 110221-1361830-009500PR). The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
Engineered allostery in light-regulated LOV-Turbo enables precise spatiotemporal control of proximity labeling in living cells.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 9:2023.03.09.531939. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.09.531939. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Methods. 2023 Jun;20(6):908-917. doi: 10.1038/s41592-023-01880-5. PMID: 36945504 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Bruder M, Polo G & Trivella DBB Natural allosteric modulators and their biological targets: molecular signatures and mechanisms. Nat. Prod. Rep 37, 488–514 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

