Epigenetic reprogramming of Runx3 reinforces CD8 + T-cell function and improves the clinical response to immunotherapy
- PMID: 37189103
- PMCID: PMC10186650
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-023-01768-0
Epigenetic reprogramming of Runx3 reinforces CD8 + T-cell function and improves the clinical response to immunotherapy
Abstract
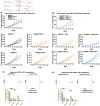
Background: Checkpoint blockade immunotherapy, represented by PD-1 or PD-L1 antibody treatment, has been of tremendous success in clinical practice. However, the low clinical response rate and lack of biomarkers for prediction of the immune response limit the clinical application of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Our recent work showed that a combination of low-dose decitabine and PD-1-ab significantly improved the complete response (CR) rate of cHL patients from 32 to 71%, which indicates that there is a significant correlation between epigenetic regulation and the clinical response to immunotherapy.
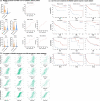
Methods: We recruited two groups of Hodgkin lymphoma patients who were treated with anti-PD-1 and DAC+anti-PD-1. CD8+ T cells were isolated from the patients' peripheral blood, DNA methylation was analyzed by EPIC, the expression profile was analyzed by RNA-seq, and multigroup analysis was performed with IPA and GSEA functional annotations. We explored the effect of DAC on the function of CD8+ T cells in the blood, spleen, tumor and lymph nodes using a mouse model. Furthermore, we explored the function of Tils in the tumor microenvironment. Then, we constructed Runx3-knockout mice to confirm the T-cell-specific function of Runx3 in CD8+ T cells and analyzed various subtypes of T cells and cytokines using mass cytometry (CyTOF).
Results: Multiomics analysis identified that DNA methylation reprogramming of Runx3 was a crucial mediator of CD8+ T-cell function. Multiomics data showed that reversal of methylation of the Runx3 promoter promoted the infiltration of CD8+ TILs and mitigated the exhaustion of CD8+ T cells. Furthermore, experiments on tissue-specific Runx3-knockout mice showed that Runx3 deficiency reduced CD8+ T infiltration and the differentiation of effector T and memory T cells. Furthermore, Runx3 deficiency significantly decreased CCR3 and CCR5 levels. Immunotherapy experiments in Runx3 conditional knockout mice showed that DAC could not reverse the resistance of anti-PD-1 in the absence of Runx3. Moreover, both our clinical data and data from TISIDB showed that Runx3 could be a potential biomarker for immunotherapy to predict the clinical response rate.
Conclusion: We demonstrate that the DNA methylation of Runx3 plays a critical role in CD8+ T-cell infiltration and differentiation during decitabine-primed PD-1-ab immunotherapy, which provides a supporting mechanism for the essential role of epiregulation in immunotherapy.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Stromal PD-L1-Positive Regulatory T cells and PD-1-Positive CD8-Positive T cells Define the Response of Different Subsets of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer to PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade Immunotherapy.J Thorac Oncol. 2018 Apr;13(4):521-532. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.11.132. Epub 2017 Dec 18. J Thorac Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29269008
-
Transcription factor RUNX3 promotes CD8+ T cell recruitment by CCL3 and CCL20 in lung adenocarcinoma immune microenvironment.J Cell Biochem. 2020 Jun;121(5-6):3208-3220. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29587. Epub 2020 Jan 3. J Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 31898342
-
Decitabine enhances tumor recognition by T cells through upregulating the MAGE-A3 expression in esophageal carcinoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Apr;112:108632. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108632. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30797153
-
Mechanisms of CD8+ T cell exclusion and dysfunction in cancer resistance to anti-PD-(L)1.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jul;163:114824. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114824. Epub 2023 May 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37141735 Review.
-
Programmed cell death 1-directed immunotherapy for enhancing T-cell function.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2013;78:239-47. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2013.78.019869. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2013. PMID: 25028401 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting pyroptosis reverses KIAA1199-mediated immunotherapy resistance in colorectal cancer.J Immunother Cancer. 2025 Feb 25;13(2):e010000. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-010000. J Immunother Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40010767 Free PMC article.
-
The tumor-intrinsic role of the m6A reader YTHDF2 in regulating immune evasion.Sci Immunol. 2024 May 31;9(95):eadl2171. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.adl2171. Epub 2024 May 31. Sci Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38820140 Free PMC article.
-
[18F]FDG PET-CT radiomics signature to predict pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer: a multicenter study.Eur Radiol. 2024 Jul;34(7):4352-4363. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-10503-8. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38127071
-
Full-length transcriptome sequencing of seven tissues of GuShi chickens.Poult Sci. 2025 Feb;104(2):104697. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104697. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39721272 Free PMC article.
-
Pim1 inactivating induces RUNX3 upregulation that improves/alleviates airway inflammation and mucus hypersecretion in vitro and in vivo.BMJ Open Respir Res. 2024 Nov 9;11(1):e002066. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2023-002066. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39521608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wei SC, et al. Fundamental mechanisms of immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Cancer Discov. 2018;8:1069–1086. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0367. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

