Tyrosinase Magnetic Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates: Biocatalytic Study in Deep Eutectic Solvent Aqueous Solutions
- PMID: 37189390
- PMCID: PMC10135570
- DOI: 10.3390/biom13040643
Tyrosinase Magnetic Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates: Biocatalytic Study in Deep Eutectic Solvent Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
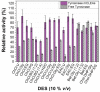
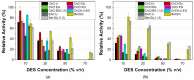
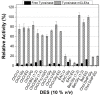
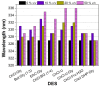
In the field of biocatalysis, the implementation of sustainable processes such as enzyme immobilization or employment of environmentally friendly solvents, like Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) are of paramount importance. In this work, tyrosinase was extracted from fresh mushrooms and used in a carrier-free immobilization towards the preparation of both non-magnetic and magnetic cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs). The prepared biocatalyst was characterized and the biocatalytic and structural traits of free tyrosinase and tyrosinase magnetic CLEAs (mCLEAs) were evaluated in numerous DES aqueous solutions. The results showed that the nature and the concentration of the DESs used as co-solvents significantly affected the catalytic activity and stability of tyrosinase, while the immobilization enhanced the activity of the enzyme in comparison with the non-immobilized enzyme up to 3.6-fold. The biocatalyst retained the 100% of its initial activity after storage at -20 °C for 1 year and the 90% of its activity after 5 repeated cycles. Tyrosinase mCLEAs were further applied in the homogeneous modification of chitosan with caffeic acid in the presence of DES. The biocatalyst demonstrated great ability in the functionalization of chitosan with caffeic acid in the presence of 10% v/v DES [Bet:Gly (1:3)], enhancing the antioxidant activity of the films.
Keywords: biocatalysis; caffeic acid; chitosan; deep eutectic solvents; enzyme; functionalization; immobilization; tyrosinase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Liu D.-M., Chen J., Shi Y.-P. Advances on Methods and Easy Separated Support Materials for Enzymes Immobilization. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018;102:332–342. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2018.03.011. - DOI
-
- De María P.D., Guajardo N., Kara S. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. Wiley; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2019. Enzyme Catalysis: In DES, with DES, and in the Presence of DES; pp. 257–271.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

