Alpha-Synuclein mRNA Level Found Dependent on L444P Variant in Carriers and Gaucher Disease Patients on Enzyme Replacement Therapy
- PMID: 37189391
- PMCID: PMC10135719
- DOI: 10.3390/biom13040644
Alpha-Synuclein mRNA Level Found Dependent on L444P Variant in Carriers and Gaucher Disease Patients on Enzyme Replacement Therapy
Abstract
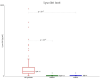
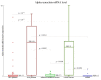
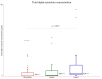
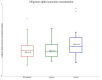
Gaucher disease (GD) is the most frequent sphingolipidosis, caused by biallelic pathogenic variants in the GBA1 gene encoding for β-glucocerebrosidase (GCase, E.C. 3.2.1.45). The condition is characterized by hepatosplenomegaly, hematological abnormalities, and bone disease in both non-neuronopathic type 1 (GD1) and neuronopathic type 3 (GD3). Interestingly, GBA1 variants were found to be one of the most important risk factors for the development of Parkinson's disease (PD) in GD1 patients. We performed a comprehensive study regarding the two most disease-specific biomarkers, glucosylsphingosine (Lyso-Gb1) and α-synuclein for GD and PD, respectively. A total of 65 patients with GD treated with ERT (47 GD1 patients and 18 GD3 patients), 19 GBA1 pathogenic variant carriers (including 10 L444P carriers), and 16 healthy subjects were involved in the study. Lyso-Gb1 was assessed by dried blood spot testing. The level of α-synuclein as an mRNA transcript, total, and oligomer protein concentration were measured with real-time PCR and ELISA, respectively. α-synuclein mRNA level was found significantly elevated in GD3 patients and L444P carriers. GD1 patients, along with GBA1 carriers of an unknown or unconfirmed variant, as well as healthy controls, have the same low level of α-synuclein mRNA. There was no correlation found between the level of α-synuclein mRNA and age in GD patients treated with ERT, whereas there was a positive correlation in L444P carriers.
Keywords: Gaucher disease; Parkinson’s disease; enzyme replacement therapy; glucosylsphingosine; α-synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gaucher Disease Diagnosis Using Lyso-Gb1 on Dry Blood Spot Samples: Time to Change the Paradigm?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 30;23(3):1627. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031627. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163551 Free PMC article.
-
A Brazilian Rare-Disease Center's Experience with Glucosylsphingosine (lyso-Gb1) in Patients with Gaucher Disease: Exploring a Novel Correlation with IgG Levels in Plasma and a Biomarker Measurement in CSF.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 1;25(5):2870. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052870. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474117 Free PMC article.
-
Lysosomal functions and dysfunctions: Molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying Gaucher disease and its association with Parkinson disease.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Aug;187:114402. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114402. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 35764179 Review.
-
A characterization of Gaucher iPS-derived astrocytes: Potential implications for Parkinson's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Feb;134:104647. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104647. Epub 2019 Nov 10. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 31669751 Free PMC article.
-
GBA1 mutations: Prospects for exosomal biomarkers in α-synuclein pathologies.Mol Genet Metab. 2020 Feb;129(2):35-46. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2019.10.006. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Mol Genet Metab. 2020. PMID: 31761523 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stirnemann J., Belmatoug N., Camou F., Serratrice C., Froissart R., Caillaud C., Levade T., Astudillo L., Serratrice J., Brassier A., et al. A Review of Gaucher Disease Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation and Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017;18:441. doi: 10.3390/ijms18020441. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

