Update on the Role of FeNO in Asthma Management
- PMID: 37189529
- PMCID: PMC10137365
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13081428
Update on the Role of FeNO in Asthma Management
Abstract
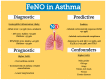
Asthma is a heterogenous disorder characterized by presence of different phenotypes and endotypes. Up to 10% of the individuals suffer from severe asthma and are at increased risk of morbidity and mortality. Fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) is a cost-effective, point of care biomarker that is used to detect type 2 airway inflammation. Guidelines have proposed to measure FeNO as an adjunct to diagnostic evaluation in individuals with suspected asthma and to monitor airway inflammation. FeNO has lower sensitivity, suggesting that it may not be a good biomarker to rule out asthma. FeNO may also be used to predict response to inhaled corticosteroids, predict adherence and deciding on biologic therapy. Higher levels of FeNO have been associated with lower lung function and increased risk for future asthma exacerbations and its predictive value increases when combined with other standard measurements of asthma assessment.
Keywords: FeNO; asthma; fractional excretion of nitric oxide; outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
N.M., D.S., A.D. and M.A. has no financial disclosures. N.A.H. received honoraria for serving as advisor or consultant for GSK, AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Regeneron, Amgen, Genentech, Novartis and Teva. His institution received research grant support of his behalf from GSK, Genentech, Sanofi, Teva, Novartis, and Astra Zeneca.
Figures
References
-
- Soriano J.B., Alemu Abajobir A., Hassen Abate K., GBD 2015 Chronic Respiratory Disease Collaborators Global, regional, and national deaths, prevalence, disability-adjusted life years, and years lived with disability for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017;5:691–706. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(17)30293-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical