The Association of Leptin with Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in End-Stage Kidney Disease Patients on Dialysis
- PMID: 37189644
- PMCID: PMC10135564
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11041026
The Association of Leptin with Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in End-Stage Kidney Disease Patients on Dialysis
Abstract
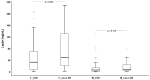
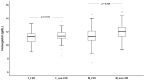
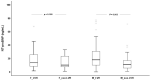
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is a common cardiovascular complication in end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) patients. We aimed at studying the association of LVH with adiponectin and leptin levels, cardiovascular stress/injury biomarkers and nutritional status in these patients. We evaluated the LV mass (LVM) and calculated the LVM index (LVMI) in 196 ESKD patients on dialysis; the levels of hemoglobin, calcium, phosphorus, parathyroid hormone, albumin, adiponectin, leptin, N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and growth differentiation factor (GDF)-15 were analyzed. ESKD patients with LVH (n = 131) presented higher NT-proBNP and GDF-15, lower hemoglobin and, after adjustment for gender, lower leptin levels compared with non-LVH patients. LVH females also showed lower leptin than the non-LVH female group. In the LVH group, LVMI presented a negative correlation with leptin and a positive correlation with NT-proBNP. Leptin emerged as an independent determinant of LVMI in both groups, and NT-proBNP in the LVH group. Low hemoglobin and leptin and increased calcium, NT-proBNP and dialysis vintage are associated with an increased risk of developing LVH. In ESKD patients on dialysis, LVH is associated with lower leptin values (especially in women), which are negatively correlated with LVMI, and with higher levels of biomarkers of myocardial stress/injury. Leptin and NT-proBNP appear as independent determinants of LVMI; dialysis vintage, hemoglobin, calcium, NT-proBNP and leptin emerged as predicting markers for LVH development. Further studies are needed to better understand the role of leptin in LVH in ESKD patients.
Keywords: GDF-15; NT-proBNP; calcium; hemoglobin; left ventricular mass index; leptin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Zoccali C., Benedetto F.A., Mallamaci F., Tripepi G., Giacone G., Cataliotti A., Seminara G., Stancanelli B., Malatino L.S. Prognostic Value of Echocardiographic Indicators of Left Ventricular Systolic Function in Asymptomatic Dialysis Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004;15:1029–1037. doi: 10.1097/01.ASN.0000117977.14912.91. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shlipak M.G., Fried L.F., Cushman M., Manolio T.A., Peterson D., Stehman-Breen C., Bleyer A., Newman A., Siscovick D., Psaty B. Cardiovascular mortality risk in chronic kidney disease: Comparison of traditional and novel risk factors. JAMA. 2005;293:1737–1745. doi: 10.1001/jama.293.14.1737. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

