The Relationship between Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus, TNF-α, and IL-10 Gene Expression
- PMID: 37189738
- PMCID: PMC10135733
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11041120
The Relationship between Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus, TNF-α, and IL-10 Gene Expression
Abstract
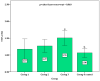
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is one of the major chronic diseases in children worldwide. This study aimed to investigate interleukin-10 (IL-10) gene expression and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) in T1DM. A total of 107 patients were included, 15 were T1DM in ketoacidosis, 30 patients had T1DM and HbA1c ≥ 8%; 32 patients had T1DM and presented HbA1c < 8%; and 30 were controls. The expression of peripheral blood mononuclear cells was performed using the reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction in real time. The cytokines gene expression was higher in patients with T1DM. The IL-10 gene expression increased substantially in patients with ketoacidosis, and there was a positive correlation with HbA1c. A negative correlation was found for IL-10 expression and the age of patients with diabetes, and the time of diagnosis of the disease. There was a positive correlation between TNF-α expression with age. The expression of IL-10 and TNF-α genes showed a significant increase in DM1 patients. Once current T1DM treatment is based on exogenous insulin, there is a need for other therapies, and inflammatory biomarkers could bring new possibilities to the therapeutic approach of the patients.
Keywords: HbA1c; gene expression; interleukin 10; ketoacidosis; tumor necrosis factor-α; type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Tenenbaum Weiss Y., Friger M., Haim A., Hershkovitz E. Patterns in Body Mass Index Changes in Children after Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Diagnosis. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. IMAJ. 2023;25:137–142. - PubMed
-
- DCCT Research Group Effects of age, duration and treatment of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus on residual beta-cell function: Observations during eligibility testing for the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT). The DCCT Research Group. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1987;65:30–36. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-1-30. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

