CRISPR-Cas System: The Current and Emerging Translational Landscape
- PMID: 37190012
- PMCID: PMC10136740
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12081103
CRISPR-Cas System: The Current and Emerging Translational Landscape
Abstract
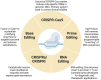
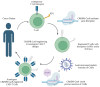
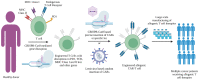
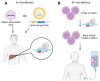
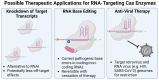
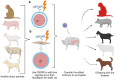
CRISPR-Cas technology has rapidly changed life science research and human medicine. The ability to add, remove, or edit human DNA sequences has transformative potential for treating congenital and acquired human diseases. The timely maturation of the cell and gene therapy ecosystem and its seamless integration with CRISPR-Cas technologies has enabled the development of therapies that could potentially cure not only monogenic diseases such as sickle cell anemia and muscular dystrophy, but also complex heterogenous diseases such as cancer and diabetes. Here, we review the current landscape of clinical trials involving the use of various CRISPR-Cas systems as therapeutics for human diseases, discuss challenges, and explore new CRISPR-Cas-based tools such as base editing, prime editing, CRISPR-based transcriptional regulation, CRISPR-based epigenome editing, and RNA editing, each promising new functionality and broadening therapeutic potential. Finally, we discuss how the CRISPR-Cas system is being used to understand the biology of human diseases through the generation of large animal disease models used for preclinical testing of emerging therapeutics.
Keywords: CRISPR animal models; CRISPR-Cas; base editors; clinical study; gene editing; prime editors; translational research.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are employees of 3M Company and declare no further conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

