The Mission of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Human Adult Renal Stem/Progenitor Cells and Renal Diseases
- PMID: 37190024
- PMCID: PMC10137190
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12081115
The Mission of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Human Adult Renal Stem/Progenitor Cells and Renal Diseases
Abstract
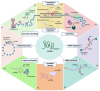
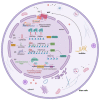
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are a large, heterogeneous class of transcripts and key regulators of gene expression at both the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels in different cellular contexts and biological processes. Understanding the potential mechanisms of action of lncRNAs and their role in disease onset and development may open up new possibilities for therapeutic approaches in the future. LncRNAs also play an important role in renal pathogenesis. However, little is known about lncRNAs that are expressed in the healthy kidney and that are involved in renal cell homeostasis and development, and even less is known about lncRNAs involved in human adult renal stem/progenitor cells (ARPC) homeostasis. Here we give a thorough overview of the biogenesis, degradation, and functions of lncRNAs and highlight our current understanding of their functional roles in kidney diseases. We also discuss how lncRNAs regulate stem cell biology, focusing finally on their role in human adult renal stem/progenitor cells, in which the lncRNA HOTAIR prevents them from becoming senescent and supports these cells to secrete high quantities of α-Klotho, an anti-aging protein capable of influencing the surrounding tissues and therefore modulating the renal aging.
Keywords: adult renal progenitor cells; lncRNA HOTAIR; long non-coding RNAs; renal disease; stem cell biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Crick F.H. On Protein Synthesis. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1958;12:138–163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

