The Functions and Phenotypes of Microglia in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 37190116
- PMCID: PMC10136897
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12081207
The Functions and Phenotypes of Microglia in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
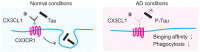
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most prevalent neurodegenerative disease worldwide, but therapeutic strategies to slow down AD pathology and symptoms have not yet been successful. While attention has been focused on neurodegeneration in AD pathogenesis, recent decades have provided evidence of the importance of microglia, and resident immune cells in the central nervous system. In addition, new technologies, including single-cell RNA sequencing, have revealed heterogeneous cell states of microglia in AD. In this review, we systematically summarize the microglial response to amyloid-β and tau tangles, and the risk factor genes expressed in microglia. Furthermore, we discuss the characteristics of protective microglia that appear during AD pathology and the relationship between AD and microglia-induced inflammation during chronic pain. Understanding the diverse roles of microglia will help identify new therapeutic strategies for AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; ApoE; CD11c; DAMs; TREM2; amyloid beta; brain; microglia; monocyte; pain; spinal cord; tau.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

