Rectal Cancer after Prostate Radiation: A Complex and Controversial Disease
- PMID: 37190143
- PMCID: PMC10136617
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15082214
Rectal Cancer after Prostate Radiation: A Complex and Controversial Disease
Abstract
A small proportion of rectal adenocarcinomas develop in patients many years after the treatment of a previous cancer using pelvic radiation, and the incidence of these rectal cancers depends on the length of follow-up from the end of radiotherapy. The risk of radiation-associated rectal cancer (RARC) is higher in patients treated with prostate external beam radiotherapy than it is in patients treated with brachytherapy. The molecular features of RARC have not been fully investigated, and survival is lower compared to non-irradiated rectal cancer patients. Ultimately, it is unclear whether the worse outcomes are related to differences in patient characteristics, treatment-related factors, or tumor biology. Radiation is widely used in the management of rectal adenocarcinoma; however, pelvic re-irradiation of RARC is challenging and carries a higher risk of treatment complications. Although RARC can develop in patients treated for a variety of malignancies, it is most common in patients treated for prostate cancer. This study will review the incidence, molecular characteristics, clinical course, and treatment outcomes of rectal adenocarcinoma in patients previously treated with radiation for prostate cancer. For clarity, we will distinguish between rectal cancer not associated with prostate cancer (RCNAPC), rectal cancer in non-irradiated prostate cancer patients (RCNRPC), and rectal cancer in irradiated prostate cancer patients (RCRPC). RARC represents a unique but understudied subset of rectal cancer, and thus requires a more comprehensive investigation in order to improve its treatment and prognosis.
Keywords: colorectal surgery; oncology; radiation; radiation oncology; radiation-associated rectal cancer; rectal cancer; surgical oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
P.B.R. received research funding from K08 CA255574 (2019) and serves as a consultant for EMD Serono (2018–2022), receives research funding from XRAD Therapeutics (2022), and is a consultant for Natera (2022). J.G.-A. receives honorariums from Johnson & Johnson, Medtronic, and Intuitive Surgical and owns stock in Intuitive Surgical. D.M.O., H.M.T., F.S.V., J.B.Y., R.R., N.R.A.B., A.L., P.B.P. and F.S.-V. have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

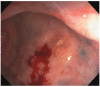
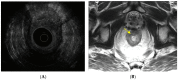
References
-
- National Cancer Institute Seer Prostate. [(accessed on 20 May 2022)]; Available online: http://seer.cancer.gov/registries/
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

