The Leading Role of Brain and Abdominal Radiological Features in the Work-Up of Anti-NMDAR Encephalitis in Children: An Up-To-Date Review
- PMID: 37190627
- PMCID: PMC10136540
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci13040662
The Leading Role of Brain and Abdominal Radiological Features in the Work-Up of Anti-NMDAR Encephalitis in Children: An Up-To-Date Review
Abstract
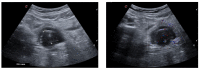
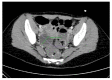
Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) encephalitis (NMDARe) is the most common cause of nonviral encephalitis, mostly affecting young women and adolescents with a strong female predominance (F/M ratio of around 4:1). NMDARe is characterized by the presence of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) antibodies against NMDARs, even though its pathophysiological mechanisms have not totally been clarified. The clinical phenotype of NMDARe is composed of both severe neurological and neuropsychiatric symptoms, including generalized seizures with desaturations, behavioral abnormalities, and movement disorders. NMDARe is often a paraneoplastic illness, mainly due to the common presence of concomitant ovarian teratomas in young women. Abdominal ultrasonography (US) is a key imaging technique that should always be performed in suspected patients. The timely use of abdominal US and the peculiar radiological features observed in NMDARe may allow for a quick diagnosis and a good prognosis, with rapid improvement after the resection of the tumor and the correct drug therapy.
Keywords: NMDARe; abdominal US; autoimmune encephalitis; encephalitis; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dalmau J., Armangué T., Planagumà J., Radosevic M., Mannara F., Leypoldt F., Geis C., Lancaster E., Titulaer M.J., Rosenfeld M.R., et al. An Update on Anti-NMDA Receptor Encephalitis for Neurologists and Psychiatrists: Mechanisms and Models. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:1045–1057. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30244-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lynch D.R., Rattelle A., Dong Y.N., Roslin K., Gleichman A.J., Panzer J.A. Anti-NMDA Receptor Encephalitis: Clinical Features and Basic Mechanisms. Adv. Pharmacol. 2018;82:235–260. - PubMed
-
- de Bruijn M.A.A.M., Aarsen F.K., van Oosterhout M.P., van der Knoop M.M., Catsman-Berrevoets C.E., Schreurs M.W.J., Bastiaansen D.E.M., Sillevis Smitt P.A.E., Neuteboom R.F., Titulaer M.J. Long-Term Neuropsychological Outcome Following Pediatric Anti-NMDAR Encephalitis. Neurology. 2018;90:e1997–e2005. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000005605. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Bruijn M.A.A.M., van Sonderen A., van Coevorden-Hameete M.H., Bastiaansen A.E.M., Schreurs M.W.J., Rouhl R.P.W., van Donselaar C.A., Majoie M.H.J.M., Neuteboom R.F., Sillevis Smitt P.A.E., et al. Evaluation of Seizure Treatment in Anti-LGI1, Anti-NMDAR, and Anti-GABABR Encephalitis. Neurology. 2019;92:e2185–e2196. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007475. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

