Effect of Post-COVID-19 on Brain Volume and Glucose Metabolism: Influence of Time Since Infection and Fatigue Status
- PMID: 37190640
- PMCID: PMC10136956
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci13040675
Effect of Post-COVID-19 on Brain Volume and Glucose Metabolism: Influence of Time Since Infection and Fatigue Status
Abstract
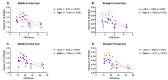
Post-COVID-19 syndrome (PCS) fatigue is typically most severe <6 months post-infection. Combining magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) imaging with the glucose analog [18F]-Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) provides a comprehensive overview of the effects of PCS on regional brain volumes and metabolism, respectively. The primary purpose of this exploratory study was to investigate differences in MRI/PET outcomes between people < 6 months (N = 18, 11 female) and > 6 months (N = 15, 6 female) after COVID-19. The secondary purpose was to assess if any differences in MRI/PET outcomes were associated with fatigue symptoms. Subjects > 6 months showed smaller volumes in the putamen, pallidum, and thalamus compared to subjects < 6 months. In subjects > 6 months, fatigued subjects had smaller volumes in frontal areas compared to non-fatigued subjects. Moreover, worse fatigue was associated with smaller volumes in several frontal areas in subjects > 6 months. The results revealed no brain metabolism differences between subjects > 6 and < 6 months. However, both groups exhibited both regional hypo- and hypermetabolism compared to a normative database. These results suggest that PCS may alter regional brain volumes but not metabolism in people > 6 months, particularly those experiencing fatigue symptoms.
Keywords: FDG-PET; brain volume; fatigue; neuroimaging in post-COVID-19; post-COVID-19.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Graham E.L., Clark J.R., Orban Z.S., Lim P.H., Szymanski A.L., Taylor C., DiBiase R.M., Jia D.T., Balabanov R., Ho S.U., et al. Persistent neurologic symptoms and cognitive dysfunction in non-hospitalized COVID-19 “long haulers”. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2021;8:1073–1085. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51350. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

