linc-mipep and linc-wrb encode micropeptides that regulate chromatin accessibility in vertebrate-specific neural cells
- PMID: 37191016
- PMCID: PMC10188112
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.82249
linc-mipep and linc-wrb encode micropeptides that regulate chromatin accessibility in vertebrate-specific neural cells
Abstract
Thousands of long intergenic non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs) are transcribed throughout the vertebrate genome. A subset of lincRNAs enriched in developing brains have recently been found to contain cryptic open-reading frames and are speculated to encode micropeptides. However, systematic identification and functional assessment of these transcripts have been hindered by technical challenges caused by their small size. Here, we show that two putative lincRNAs (linc-mipep, also called lnc-rps25, and linc-wrb) encode micropeptides with homology to the vertebrate-specific chromatin architectural protein, Hmgn1, and demonstrate that they are required for development of vertebrate-specific brain cell types. Specifically, we show that NMDA receptor-mediated pathways are dysregulated in zebrafish lacking these micropeptides and that their loss preferentially alters the gene regulatory networks that establish cerebellar cells and oligodendrocytes - evolutionarily newer cell types that develop postnatally in humans. These findings reveal a key missing link in the evolution of vertebrate brain cell development and illustrate a genetic basis for how some neural cell types are more susceptible to chromatin disruptions, with implications for neurodevelopmental disorders and disease.
Keywords: behavior; cell identity; developmental biology; gene regulation; micropeptides; neurodevelopment; neuroscience; single cell analyses; zebrafish.
© 2023, Tornini et al.
Conflict of interest statement
VT, LM, HL, TG, SD, VS, FK, YT, KD, MK, CV, AB, JR, AG No competing interests declared, SK Reviewing editor, eLife
Figures



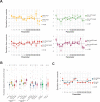
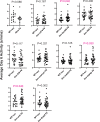




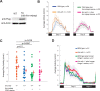





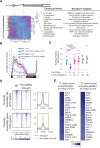










Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2022.07.21.501032
References
-
- Abuhatzira L, Shamir A, Schones DE, Schäffer AA, Bustin M. The chromatin-binding protein HMGN1 regulates the expression of methyl CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2) and affects the behavior of mice. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2011;286:42051–42062. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.300541. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barlow IL, Mackay E, Wheater E, Goel A, Lim S, Zimmerman S, Woods I, Prober DA, Rihel J. A Genetic Screen Identifies Dreammist as A Regulator of Sleep. bioRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.11.18.388736. - DOI
-
- Bazzini AA, Johnstone TG, Christiano R, Mackowiak SD, Obermayer B, Fleming ES, Vejnar CE, Lee MT, Rajewsky N, Walther TC, Giraldez AJ. Identification of small ORFs in vertebrates using ribosome footprinting and evolutionary conservation. The EMBO Journal. 2014;33:981–993. doi: 10.1002/embj.201488411. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- SRA/SRA314809
- SRA/SRP034750
- SRA/SRP072296
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

