An Amino Acid Substitution in Elongation Factor EF-G1A Alters the Antibiotic Susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa LasR-Null Mutants
- PMID: 37191503
- PMCID: PMC10294626
- DOI: 10.1128/jb.00114-23
An Amino Acid Substitution in Elongation Factor EF-G1A Alters the Antibiotic Susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa LasR-Null Mutants
Abstract
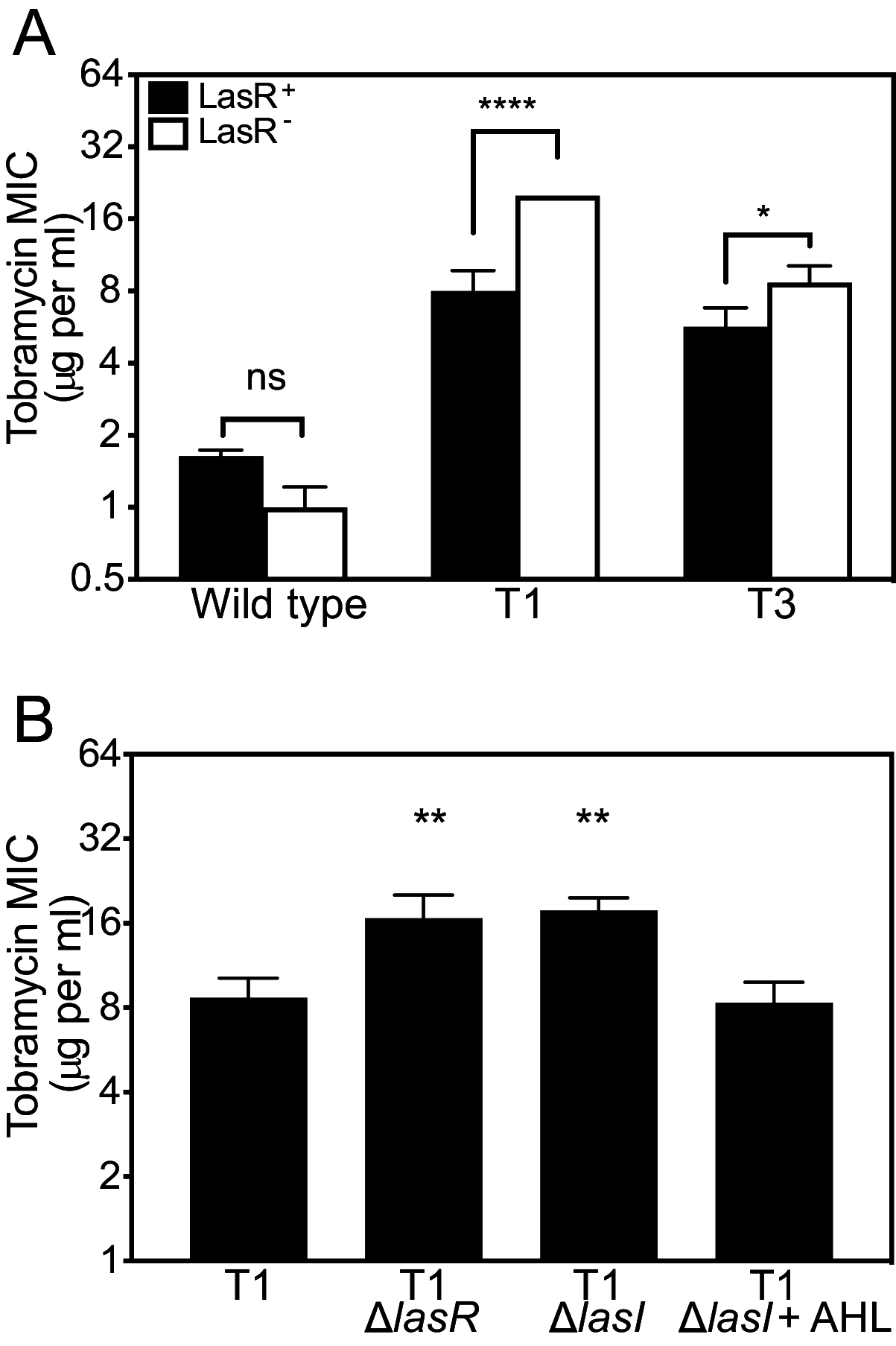
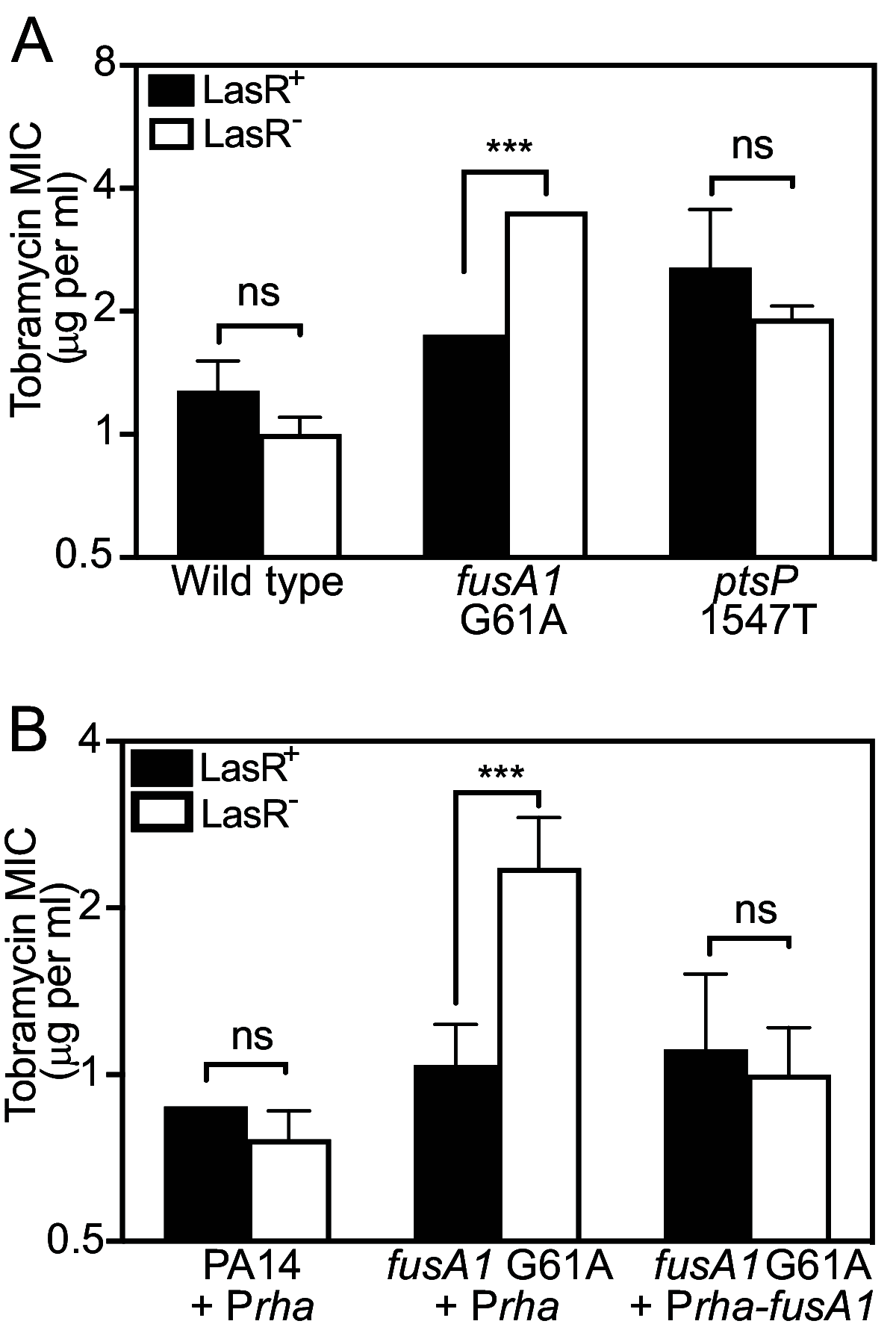
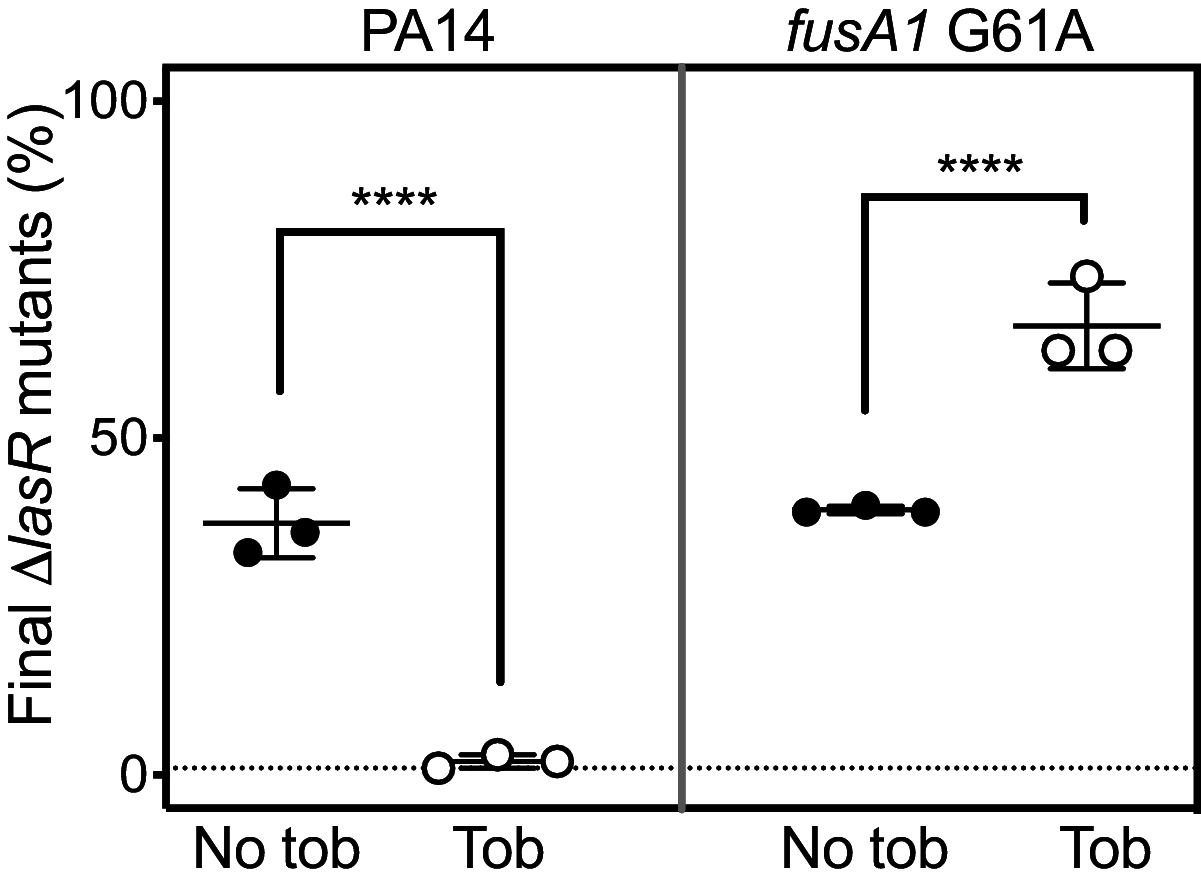
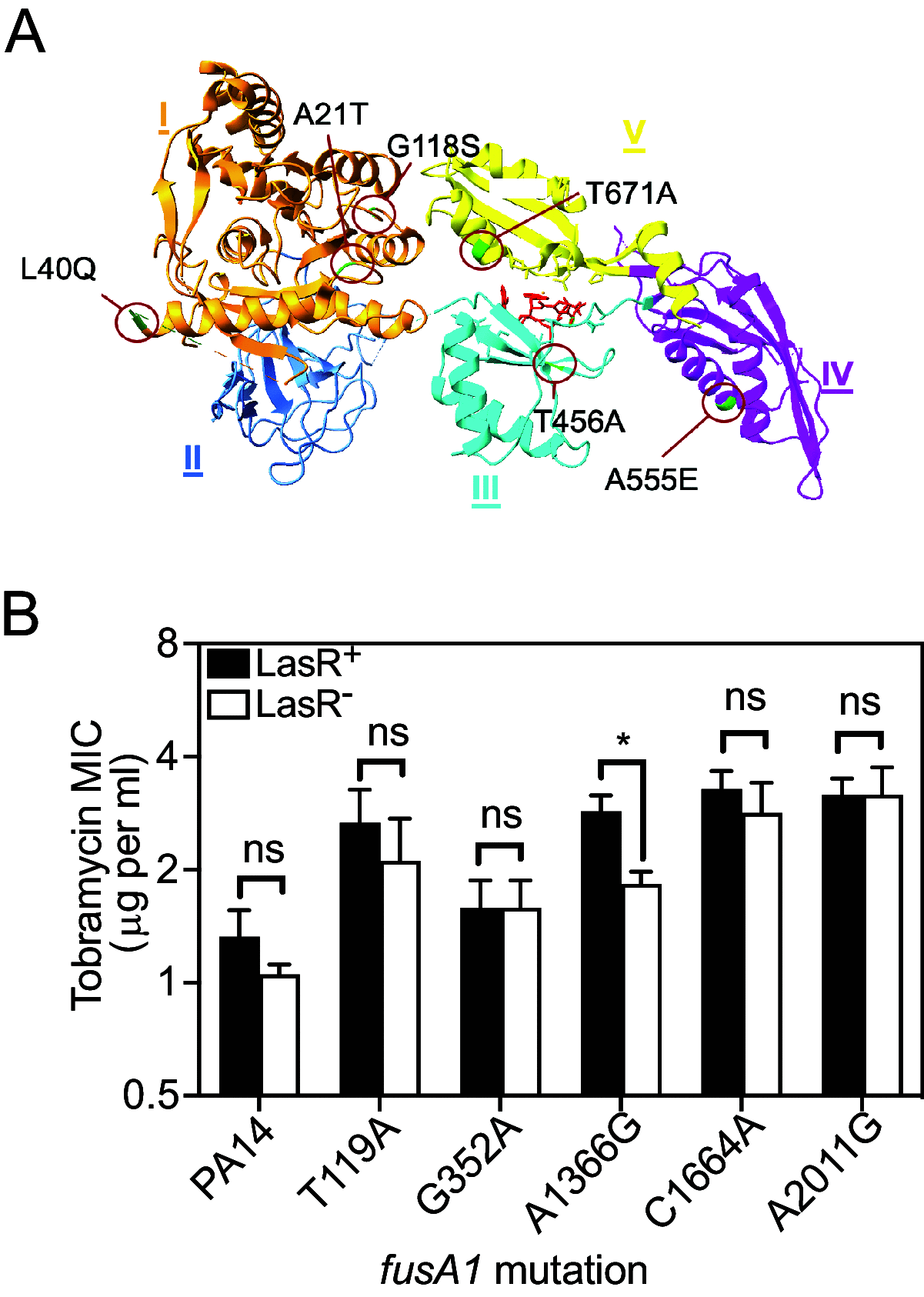
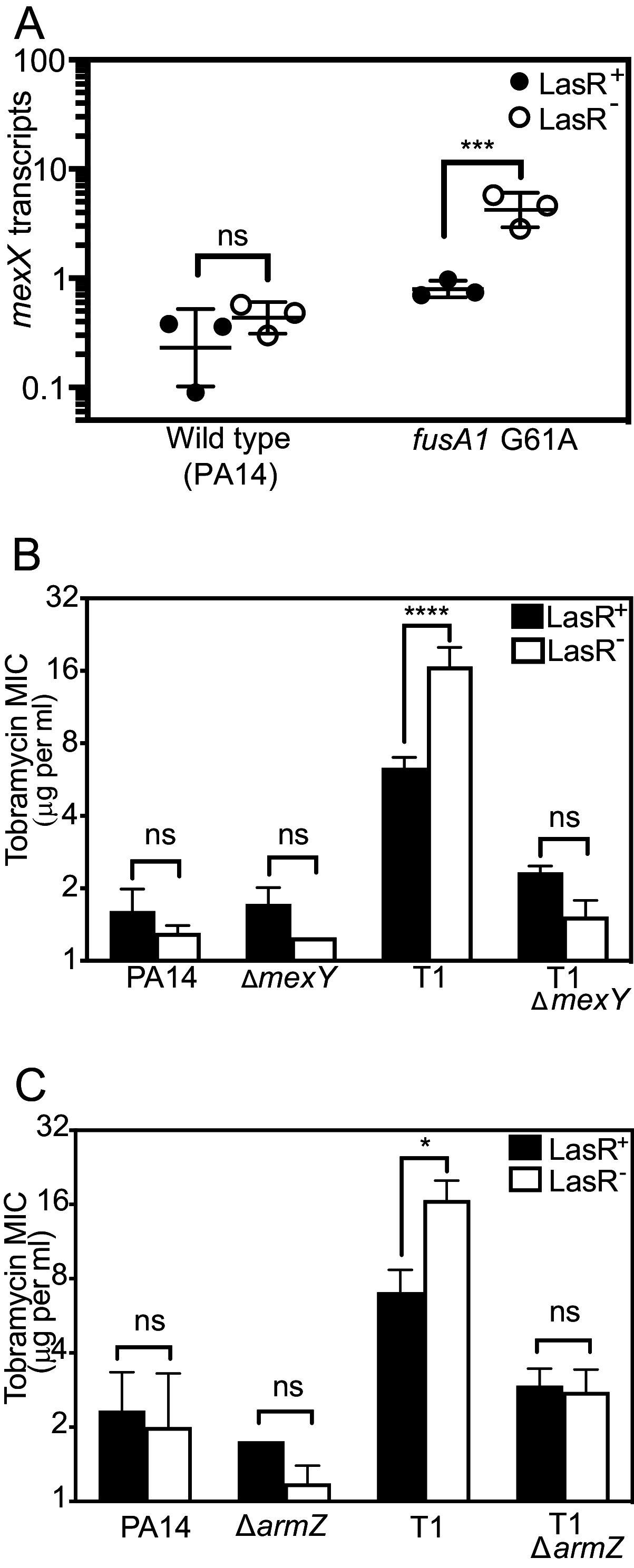
The opportunistic bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa uses the LasR-I quorum-sensing system to increase resistance to the aminoglycoside antibiotic tobramycin. Paradoxically, lasR-null mutants are commonly isolated from chronic human infections treated with tobramycin, suggesting there may be a mechanism that permits the emergence of lasR-null mutants under tobramycin selection. We hypothesized that some other genetic mutations that emerge in these isolates might modulate the effects of lasR-null mutations on antibiotic resistance. To test this hypothesis, we inactivated lasR in several highly tobramycin-resistant isolates from long-term evolution experiments. In some of these isolates, inactivating lasR further increased resistance, compared with decreasing resistance of the wild-type ancestor. These strain-dependent effects were due to a G61A nucleotide polymorphism in the fusA1 gene encoding amino acid substitution A21T in the translation elongation factor EF-G1A. The EF-G1A mutational effects required the MexXY efflux pump and the MexXY regulator ArmZ. The fusA1 mutation also modulated ΔlasR mutant resistance to two other antibiotics, ciprofloxacin and ceftazidime. Our results identify a gene mutation that can reverse the direction of the antibiotic selection of lasR mutants, a phenomenon known as sign epistasis, and provide a possible explanation for the emergence of lasR-null mutants in clinical isolates. IMPORTANCE One of the most common mutations in Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates is in the quorum sensing lasR gene. In laboratory strains, lasR disruption decreases resistance to the clinical antibiotic tobramycin. To understand how lasR mutations emerge in tobramycin-treated patients, we mutated lasR in highly tobramycin-resistant laboratory strains and determined the effects on resistance. Disrupting lasR enhanced the resistance of some strains. These strains had a single amino acid substitution in the translation factor EF-G1A. The EF-G1A mutation reversed the selective effects of tobramycin on lasR mutants. These results illustrate how adaptive mutations can lead to the emergence of new traits in a population and are relevant to understanding how genetic diversity contributes to the progression of disease during chronic infections.
Keywords: LasR; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; antibiotic resistance; evolution; quorum sensing; tobramycin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Update of
-
Tobramycin adaptation alters the antibiotic susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing-null mutants.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 19:2023.01.13.523864. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.13.523864. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Bacteriol. 2023 Jun 27;205(6):e0011423. doi: 10.1128/jb.00114-23. PMID: 36711731 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

