Building a collaborative cloud platform to accelerate heart, lung, blood, and sleep research
- PMID: 37192819
- PMCID: PMC10280347
- DOI: 10.1093/jamia/ocad048
Building a collaborative cloud platform to accelerate heart, lung, blood, and sleep research
Abstract
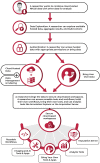
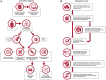
Research increasingly relies on interrogating large-scale data resources. The NIH National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute developed the NHLBI BioData CatalystⓇ (BDC), a community-driven ecosystem where researchers, including bench and clinical scientists, statisticians, and algorithm developers, find, access, share, store, and compute on large-scale datasets. This ecosystem provides secure, cloud-based workspaces, user authentication and authorization, search, tools and workflows, applications, and new innovative features to address community needs, including exploratory data analysis, genomic and imaging tools, tools for reproducibility, and improved interoperability with other NIH data science platforms. BDC offers straightforward access to large-scale datasets and computational resources that support precision medicine for heart, lung, blood, and sleep conditions, leveraging separately developed and managed platforms to maximize flexibility based on researcher needs, expertise, and backgrounds. Through the NHLBI BioData Catalyst Fellows Program, BDC facilitates scientific discoveries and technological advances. BDC also facilitated accelerated research on the coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.
Keywords: cloud computing; data analysis; data-driven science; reproducibility of results; team science.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Medical Informatics Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures

References
-
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NHLBI's COVID-19 Research Strategy. National Heart Lung and Blood Institute, 2021. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/coronavirus/research-strategy. Accessed March 31, 2023.
-
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Cure sickle cell initiative: advancing research in sickle cell disease: cure sickle cell. Cure Sickle Cell Initiative | Advancing research in sickle cell disease | Cure Sickle Cell. 2023. https://curesickle.org/. Accessed March 31, 2023.
-
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Collaborating Network of Networks for Evaluating COVID-19 and Therapeutic Strategies (CONNECTS). National Heart Lung and Blood Institute, n.d. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/science/collaborating-network-networks-evaluat....
-
- Powell K. The broken promise that undermines human genome research. Nature News. February 10, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-00331-5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

