Hexokinases in cancer and other pathologies
- PMID: 37192912
- PMCID: PMC10120283
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellin.2023.100077
Hexokinases in cancer and other pathologies
Abstract
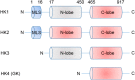
Glucose metabolism is indispensable for cell growth and survival. Hexokinases play pivotal roles in glucose metabolism through canonical functions of hexokinases as well as in immune response, cell stemness, autophagy, and other cellular activities through noncanonical functions. The aberrant regulation of hexokinases contributes to the development and progression of pathologies, including cancer and immune diseases.
Keywords: Cancer; Glucose metabolism; Glycolysis; Hexokinase; Immune diseases; Protein kinase.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Agius L. The physiological role of glucokinase binding and translocation in hepatocytes. Advances in Enzyme Regulation. 1998;38:303–331. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

