Relationship between BCL2 mutations and follicular lymphoma outcome in the chemoimmunotherapy era
- PMID: 37193683
- PMCID: PMC10188323
- DOI: 10.1038/s41408-023-00847-1
Relationship between BCL2 mutations and follicular lymphoma outcome in the chemoimmunotherapy era
Abstract
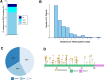
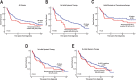
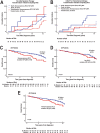
How to identify follicular lymphoma (FL) patients with low disease burden but high risk for early progression is unclear. Building on a prior study demonstrating the early transformation of FLs with high variant allele frequency (VAF) BCL2 mutations at activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AICDA) sites, we examined 11 AICDA mutational targets, including BCL2, BCL6, PAX5, PIM1, RHOH, SOCS, and MYC, in 199 newly diagnosed grade 1 and 2 FLs. BCL2 mutations with VAF ≥20% occurred in 52% of cases. Among 97 FL patients who did not initially receive rituximab-containing therapy, nonsynonymous BCL2 mutations at VAF ≥20% were associated with increased transformation risk (HR 3.01, 95% CI 1.04-8.78, p = 0.043) and a trend toward shorter event-free survival (EFS, median 20 months with mutations versus 54 months without, p = 0.052). Other sequenced genes were less frequently mutated and did not increase the prognostic value of the panel. Across the entire population, nonsynonymous BCL2 mutations at VAF ≥20% were associated with decreased EFS (HR 1.55, 95% CI 1.02-2.35, p = 0.043 after correction for FLIPI and treatment) and decreased overall survival after median 14-year follow-up (HR 1.82, 95% CI 1.05-3.17, p = 0.034). Thus, high VAF nonsynonymous BCL2 mutations remain prognostic even in the chemoimmunotherapy era.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.L.F. has received research funding from Seattle Genetics, is an inventor of technology for which Mayo Clinic holds unlicensed patents, and is an inventor of intellectual property licensed to Zeno Pharmaceuticals. J.R.C. has received research funding from Genentech. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

