Role and mechanistic actions of protein kinase inhibitors as an effective drug target for cancer and COVID
- PMID: 37193831
- PMCID: PMC10188327
- DOI: 10.1007/s00203-023-03559-z
Role and mechanistic actions of protein kinase inhibitors as an effective drug target for cancer and COVID
Abstract
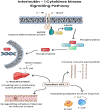
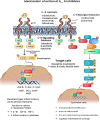
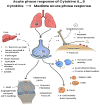
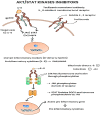
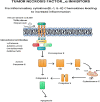
Kinases can be grouped into 20 families which play a vital role as a regulator of neoplasia, metastasis, and cytokine suppression. Human genome sequencing has discovered more than 500 kinases. Mutations of the kinase itself or the pathway regulated by kinases leads to the progression of diseases such as Alzheimer's, viral infections, and cancers. Cancer chemotherapy has made significant leaps in recent years. The utilization of chemotherapeutic agents for treating cancers has become difficult due to their unpredictable nature and their toxicity toward the host cells. Therefore, targeted therapy as a therapeutic option against cancer-specific cells and toward the signaling pathways is a valuable avenue of research. SARS-CoV-2 is a member of the Betacoronavirus genus that is responsible for causing the COVID pandemic. Kinase family provides a valuable source of biological targets against cancers and for recent COVID infections. Kinases such as tyrosine kinases, Rho kinase, Bruton tyrosine kinase, ABL kinases, and NAK kinases play an important role in the modulation of signaling pathways involved in both cancers and viral infections such as COVID. These kinase inhibitors consist of multiple protein targets such as the viral replication machinery and specific molecules targeting signaling pathways for cancer. Thus, kinase inhibitors can be used for their anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic activity along with cytokine suppression in cases of COVID. The main goal of this review is to focus on the pharmacology of kinase inhibitors for cancer and COVID, as well as ideas for future development.
Keywords: COVID; Cancer; Chronic inflammatory response; Cytokines; Protein kinases.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abourehab MAS, Alqahtani AM, Youssif BGM, Gouda AM. Globally approved EGFR inhibitors: insights into their syntheses, target kinases, biological activities, receptor interactions, and metabolism. Molecules. 2021;26(21):6677. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216677.PMID:34771085;PMCID:PMC8587155. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

