Comprehensive analysis of m6A related gene mutation characteristics and prognosis in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 37194014
- PMCID: PMC10186803
- DOI: 10.1186/s12920-023-01509-8
Comprehensive analysis of m6A related gene mutation characteristics and prognosis in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer is considered as the second most common cancer worldwide. Studies have shown that m6A RNA methylation abnormalities play an important role in the pathogenesis of many human diseases, including cancer. The current study was designed to characterize the mutation of m6A related genes and explore their prognostic role in colorectal cancer.
Methods: RNA-seq data and somatic mutation data of TCGA-COAD and TCGA-READ were downloaded from UCSC xena for comprehensive analysis. M6A related genes were selected from previous literatures, including "Writer" protein (METTL3, METTL5, METTL14, METTL16, ZC3H13, RBM15, WTAP, KIAA1429), "Reader" protein YTHDF1, YTHDF2, YTHDF3, YTHDC1, YTHDC2, HNRNPC, IGF2BP1, IGF2BP2, IGF2BP3), and "Eraser" protein (FTO, ALKBH5). Kaplan-Meier diagrams were used to explore the correlation between m6A-related genes and colorectal cancer prognosis. The correlations between m6A-related genes and clinical parameters and immune-related indicators were explored by Spearman correlation analysis. And finally, the expression patterns of five key genes (RBMX, FMR1, IGF2BP1, LRPPRC and YTHDC2) were detected by qPCR in CRC specimens.
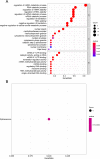
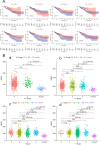
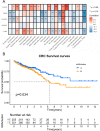
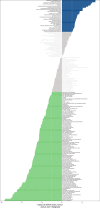
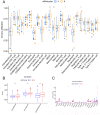
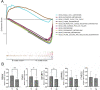
Results: In CRC, the expressions of m6A-related genes were significantly different between CRC and normal control except METTL14, YTHDF2, YTHDF3. Some of CRC patients (178 in 536) have a m6A-related genes mutation. ZC3H13 has highest mutation frequency of all m6A-related genes. M6A-related genes mainly enrich in regulation of mRNA metabolic process pathway. Patients with high expressions of FMR1, LRPPRC, METTL14, RBMX, YTHDC2, YTHDF2, YTHDF3 have poor prognosis in CRC. There was a significant correlation between the FMR1, LRPPRC, RBMX, YTHDC2, IGF2BP1 expression and the clinical characteristics of CRC. In addition, these genes are significantly associated with immune-related indicators. According to the expression patterns of FMR1, LRPPRC, RBMX, YTHDC2, and IGF2BP1, patients with CRC were clustered into two groups, and their survival was significantly different. By evaluating the tumor microenvironment in two clusters using ssGSEA, expressions of immune checkpoints and GSVA enrichment analysis, we observed that the immune and stem cell index of two cluster were much different. The qPCR results showed that RBMX expression was markedly elevated in cancerous tissues than in the normal colonic tissues.
Conclusion: Our study identified novel prognostic markers associated with immune of CRC cancer patients. Moreover, the potential mechanisms of prognostic markers in regulating the etiology of CRC cancer were investigated. These findings enrich our understanding of the relationships between m6a related genes and CRC, and may provide novel ideas in the therapy of CRC patients.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Immune; Prognosis; m6A.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Shi JF, Wang L, Ran JC, Wang H, Liu CC, Zhang HZ, Yang L, Shi SS, Jiang LM, Fan JH, Zhang YM, Wang WH, Ren JS, Zhu L, Zheng ZX, Sun YK, Zou SM, Jiang J, Chen B, Chen HD, Liu GX, Yang L, Huang YC, Guo LW, Wang DB, Zhang YZ, Mao AY, Wang JL, Gong JY, Wei DH, Qiu WQ, Song BB, Zhang K, Li N, Feletto E, Lew JB, Qiao YL, Chen WQ, Dai M, He J. Clinical characteristics, medical service utilization, and expenditure for colorectal cancer in China, 2005 to 2014: overall design and results from a multicenter retrospective epidemiologic survey. Cancer. 2021;127(11):1880–1893. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33445. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rosander E, Holm T, Sjövall A, Hjern F, Weibull CE, Nordenvall C. Preoperative multidisciplinary team assessment is associated with improved survival in patients with locally advanced colon cancer; a nationwide cohort study in 3157 patients. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2021;47(9):2398–2404. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2021.05.008. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

