Comparison of postoperative analgesic effects of erector spinae plane block and quadratus lumborum block in laparoscopic liver resection: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 37194102
- PMCID: PMC10186739
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-023-07341-w
Comparison of postoperative analgesic effects of erector spinae plane block and quadratus lumborum block in laparoscopic liver resection: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Compared with open surgery, laparoscopic liver resection is a minimally invasive surgical technique. However, a number of patients experience moderate-to-severe postoperative pain after laparoscopic liver resection. This study aims to compare the postoperative analgesic effects of erector spinae plane block (ESPB) and quadratus lumborum block (QLB) in patients undergoing laparoscopic liver resection.
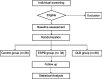
Methods: One hundred and fourteen patients undergoing laparoscopic liver resection will be randomly allocated to three groups (control, ESPB, or QLB) in a 1:1:1 ratio. In the control group, participants will receive systemic analgesia consisting of regular NSAIDs and fentanyl-based patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) according to the institutional postoperative analgesia protocol. In the two experimental groups (ESPB or QLB group), the participants will receive preoperative bilateral ESPB or bilateral QLB in addition to systemic analgesia according to the institutional protocol. ESPB will be performed at the 8th thoracic vertebra level with ultrasound guidance before surgery. QLB will be performed in the supine position on the posterior plane of the quadratus lumborum with ultrasound guidance before surgery. The primary outcome is cumulative opioid consumption 24 h after surgery. Secondary outcomes are cumulative opioid consumption, pain severity, opioid-related adverse events, and block-related adverse events at predetermined time points (24, 48, and 72 h after surgery). Differences in plasma ropivacaine concentrations in the ESPB and QLB groups would be investigated, and the quality of postoperative recovery among the groups will be compared.
Discussion: This study will reveal the usefulness of ESPB and QLB in terms of postoperative analgesic efficacy and safety in patients undergoing laparoscopic liver resection. Additionally, the study results will provide information on the analgesic superiority of ESPB versus QLB in the same population.
Trial registration: Prospectively registered with the Clinical Research Information Service on August 3, 2022; KCT0007599.
Keywords: Erector spinae plane block; Hepatectomy; Laparoscopy; Pain; Postoperative; Quadratus lumborum block.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ultrasound-Guided Techniques for Postoperative Analgesia in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy: Erector Spinae Plane Block vs. Quadratus Lumborum Block.Pain Physician. 2023 May;26(3):245-256. Pain Physician. 2023. PMID: 37192227 Clinical Trial.
-
Quadratus lumborum and erector spinae plane blocks are effective for analgesia in laparoscopic hysterectomy: a randomized controlled trial.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023 Dec;27(23):11323-11333. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202312_34571. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38095381 Clinical Trial.
-
Erector spinae plane block versus quadratus lumborum block for postoperative analgesia after laparoscopic nephrectomy: A randomized controlled trial.J Clin Anesth. 2024 Sep;96:111466. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2024.111466. Epub 2024 Apr 26. J Clin Anesth. 2024. PMID: 38677191 Clinical Trial.
-
Erector spinae plane block for laparoscopic surgeries: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Oct 29;24(1):389. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02775-4. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 39472781 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-guided erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia in patients after liver surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis on randomized comparative studies.Int J Surg. 2022 Jul;103:106689. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2022.106689. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Int J Surg. 2022. PMID: 35662584
Cited by
-
Opioid-free anesthesia with ultrasound-guided quadratus lumborum block in the supine position for lower abdominal or pelvic surgery: a randomized controlled trial.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 26;14(1):4652. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55370-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38409359 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Wakabayashi G, Cherqui D, Geller DA, Buell JF, Kaneko H, Han HS, Asbun H, O'Rourke N, Tanabe M, Koffron AJ. Recommendations for laparoscopic liver resection: a report from the second international consensus conference held in Morioka. Ann Surg. 2015;261(4):619–629. - PubMed
-
- Kim D, Kim JM, Choi G-S, Heo G, Kim GS, Jeong JS. Ultrasound-guided erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia in laparoscopic liver resection: a prospective, randomised controlled, patient and observer-blinded study. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2021;38:S106–S112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

