Super-High Magnification Dermoscopy Can Help for the Diagnosis of Lentigo Maligna: a Pilot Study on 61 Cases
- PMID: 37196274
- PMCID: PMC10188132
- DOI: 10.5826/dpc.1302a101
Super-High Magnification Dermoscopy Can Help for the Diagnosis of Lentigo Maligna: a Pilot Study on 61 Cases
Abstract
Introduction: Facial lentigo maligna/lentigo maligna melanoma (LM/LMM) is a significant diagnostic clinical challenge and dermoscopy can help its diagnosis.
Objectives: The following study aimed to evaluate if super-high magnification dermoscopy at 400x can add further details for the diagnosis of the LM/LMM.
Methods: This is a retrospective observational, multicentric study enrolling patients who received a 20x and 400x (D400) magnification dermoscopic examination of facial skin lesions in clinical differential diagnosis with LM/LMM. Dermoscopic images were retrospectively evaluated by four observers for the presence/absence of nine 20x and ten 400x dermoscopic features. Univariate and multivariate analyses were carried out to find predictors of LM/LMM.
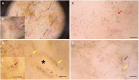
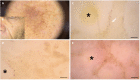
Results: We enrolled 61 patients with a single atypical skin lesion of the face, including 23 LMs and 3 LMMs. The presence of roundish and/or dendritic melanocytes (P < 0.001), irregular arrangement of melanocytes (P <0.001), irregular in shape and size melanocytes (P = 0.002), and folliculotropism of melanocytes (P <0.001) at D400 were more frequent in LM/LMM than other facial lesions. According to the multivariate analysis, roundish melanocytes at 400x dermoscopy were more indicative of LM/ LMM (Odds Ratio-OR 49.25, 95% CI 8.75-513.2, P < 0.001), and sharply demarcated borders at 20x dermoscopy were more indicative of not-LM/LMM (OR 0.1, 95% CI 0.01-0.79, P = 0.038).
Conclusions: D400 can identify atypical melanocyte proliferation and folliculotropism that can help to identify LM/LMM together with conventional dermoscopy data. Our preliminary observations should be confirmed by larger studies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Zoom-in Dermoscopy for Facial Tumors.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jan 30;15(3):324. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15030324. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39941253 Free PMC article.
-
Lentigo maligna and lentigo maligna melanoma in vivo differentiation with dermoscopy and reflectance confocal microscopy: A retrospective, multicentre study.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023 Nov;37(11):2293-2300. doi: 10.1111/jdv.19291. Epub 2023 Jul 21. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023. PMID: 37357442
-
Super-High Magnification Dermoscopy in 190 Clinically Atypical Pigmented Lesions.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jun 30;13(13):2238. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13132238. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37443632 Free PMC article.
-
Reviewing Challenges in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Lentigo Maligna and Lentigo-Maligna Melanoma.Rare Cancers Ther. 2015;3(1):133-145. doi: 10.1007/s40487-015-0012-9. Epub 2015 Oct 15. Rare Cancers Ther. 2015. PMID: 27182482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of In Vivo Reflectance Confocal Microscopy in the Analysis of Melanocytic Lesions.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018 Apr;26(1):64-67. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018. PMID: 29782304 Review.
Cited by
-
Optical super-high magnification dermoscopy versus standard dermoscopy in basal cell carcinoma.An Bras Dermatol. 2025 Jul-Aug;100(4):501152. doi: 10.1016/j.abd.2025.501152. Epub 2025 Jul 3. An Bras Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40614547 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Zoom-in Dermoscopy for Facial Tumors.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jan 30;15(3):324. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15030324. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39941253 Free PMC article.
-
Optical super-high magnification dermoscopy of benign and malignant melanocytic lesions in correlation with histopathology.J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2025 May;23(5):610-619. doi: 10.1111/ddg.15640. Epub 2025 Feb 28. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2025. PMID: 40018765 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay JSH, Bray F, et al. GLoBoCanN Cancer incidence and mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No 10. Lyon, France: international agency for Research on Cancer; 2010. [last accessed 1 December 2021]. Available from: http://globocan.iarc.fr.
-
- Rapporto AIOM-AIRT 2017. [last accessed 1 December 2021]. Available from: http://media.aiom.it/userfiles/files/doc/documenti_scientifici/2017_nume....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
