Methylprednisolone alleviates cognitive functions through the regulation of neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 37197654
- PMCID: PMC10183590
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1192940
Methylprednisolone alleviates cognitive functions through the regulation of neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
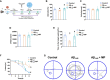
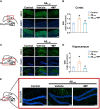
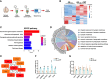
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease and linked to abnormal deposition of amyloid-β (Aβ), neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs), synaptic dysfunction, and neuroinflammation. Despite significant progress in unravelling the pathogenesis of AD, currently main therapeutic interventions is limited to symptomatic alleviation. Methylprednisolone (MP), a synthetic glucocorticoid, is recognized for its extensive anti-inflammatory properties. Our study assessed the neuroprotective effect of MP (25 mg/kg) administration to an Aβ1-42-induced AD mouse model. Our findings demonstrate that MP treatment can ameliorate cognitive impairment in Aβ1-42-induced AD mice and suppress microglial activation in the cortex and hippocampus. RNA-Sequencing analysis reveals that MP ultimately rescues cognitive dysfunction through improving the synapse function and inhibiting the immune and inflammatory processes. Our study suggests that MP could be a promising drug alternative for the treatment of AD, either alone or in combination with other existing drugs.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; cognitive function; methylprednisolone; microglial activation; neuroinflammation.
Copyright © 2023 Sun, Li, A, Li, Zhong, Chen, Liu, Zhang, Zhu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hydrocortisone Mitigates Alzheimer's-Related Cognitive Decline through Modulating Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation.Cells. 2023 Sep 25;12(19):2348. doi: 10.3390/cells12192348. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37830561 Free PMC article.
-
Patchouli alcohol attenuates the cognitive deficits in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease via modulating neuropathology and gut microbiota through suppressing C/EBPβ/AEP pathway.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Jan 30;20(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02704-1. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 36717922 Free PMC article.
-
Mulberry Fruit Extract Alleviates Cognitive Impairment by Promoting the Clearance of Amyloid-β and Inhibiting Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's Disease Mice.Neurochem Res. 2020 Sep;45(9):2009-2019. doi: 10.1007/s11064-020-03062-7. Epub 2020 Jun 1. Neurochem Res. 2020. PMID: 32488469
-
Microglial modulation as a therapeutic strategy in Alzheimer's disease: Focus on microglial preconditioning approaches.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Aug;28(15):e18554. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18554. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39103747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potentials of plant iridoids in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: A review.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 May 1;169:185-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30877973 Review.
Cited by
-
Asiaticoside Mitigates Alzheimer's Disease Pathology by Attenuating Inflammation and Enhancing Synaptic Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 26;24(15):11976. doi: 10.3390/ijms241511976. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569347 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted drug delivery into glial scar using CAQK peptide in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis.Brain Commun. 2023 Nov 27;5(6):fcad325. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcad325. eCollection 2023. Brain Commun. 2023. PMID: 38107502 Free PMC article.
-
Compensatory enhancement of orexinergic system functionality induced by amyloid-β protein: a neuroprotective response in Alzheimer's disease.Front Physiol. 2025 Mar 24;16:1529981. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1529981. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40196718 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrocortisone Mitigates Alzheimer's-Related Cognitive Decline through Modulating Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation.Cells. 2023 Sep 25;12(19):2348. doi: 10.3390/cells12192348. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37830561 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

