Computational pathology improves risk stratification of a multi-gene assay for early stage ER+ breast cancer
- PMID: 37198173
- PMCID: PMC10192429
- DOI: 10.1038/s41523-023-00545-y
Computational pathology improves risk stratification of a multi-gene assay for early stage ER+ breast cancer
Abstract
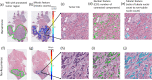
Prognostic markers currently utilized in clinical practice for estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) and lymph node-negative (LN-) invasive breast cancer (IBC) patients include the Nottingham grading system and Oncotype Dx (ODx). However, these biomarkers are not always optimal and remain subject to inter-/intra-observer variability and high cost. In this study, we evaluated the association between computationally derived image features from H&E images and disease-free survival (DFS) in ER+ and LN- IBC. H&E images from a total of n = 321 patients with ER+ and LN- IBC from three cohorts were employed for this study (Training set: D1 (n = 116), Validation sets: D2 (n = 121) and D3 (n = 84)). A total of 343 features relating to nuclear morphology, mitotic activity, and tubule formation were computationally extracted from each slide image. A Cox regression model (IbRiS) was trained to identify significant predictors of DFS and predict a high/low-risk category using D1 and was validated on independent testing sets D2 and D3 as well as within each ODx risk category. IbRiS was significantly prognostic of DFS with a hazard ratio (HR) of 2.33 (95% confidence interval (95% CI) = 1.02-5.32, p = 0.045) on D2 and a HR of 2.94 (95% CI = 1.18-7.35, p = 0.0208) on D3. In addition, IbRiS yielded significant risk stratification within high ODx risk categories (D1 + D2: HR = 10.35, 95% CI = 1.20-89.18, p = 0.0106; D1: p = 0.0238; D2: p = 0.0389), potentially providing more granular risk stratification than offered by ODx alone.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.M. is an equity holder in Elucid Bioimaging and in Inspirata Inc. In addition, he has served as a scientific advisory board member for Inspirata Inc, Astrazeneca, Bristol Meyers-Squibb and Merck. Currently he serves on the advisory board of Aiforia Inc. He also has sponsored research agreements with Philips and Bristol Meyers-Squibb. His technology has been licensed to Elucid Bioimaging. He is also involved in a NIH U24 grant with PathCore Inc, and three different R01 grants with Inspirata Inc. S.G. has consulted for Merck, Roche, Foundation Medicine, Foghorn Therapeutics, Inspirata, Novartis and EQRX. He is also on the Scientific Advisory Board of Silagene. In addition, he has equity in Silagene and Inspirata and research funding from M2Gen. His spouse is an employee of Merck and has equity in Merck. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Grants and funding
- R01 CA216579/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR012463/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R43 EB028736/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA239055/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA249992/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233328/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA220581/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA202752/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA208236/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA248226/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX004121/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 CA257612/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA254566/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

