Pharmacological inhibition of BCL-2 with the FDA-approved drug venetoclax impairs longitudinal bone growth
- PMID: 37198212
- PMCID: PMC10192431
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-34965-4
Pharmacological inhibition of BCL-2 with the FDA-approved drug venetoclax impairs longitudinal bone growth
Abstract
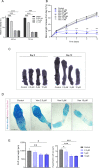
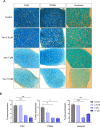
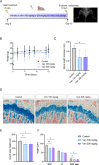
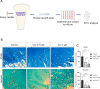
Treatment-related skeletal complications are common in childhood cancer patients and survivors. Venetoclax is a BCL-2 inhibitor that has shown efficacy in hematological malignancies in adults and is being investigated in pediatric cancer clinical trials as a promising therapeutic modality. Venetoclax triggers cell death in cancer cells, but whether it exerts similar effects in normal bone cells, is unknown. Chondrogenic ATDC5 cells, E20 fetal rat metatarsal bones, and human growth plate biopsies were treated with different concentrations of venetoclax. Female NMRI nu/nu mice were treated with venetoclax or vehicle for 15 days. Mice were X-rayed at baseline and at the end of the experiment to assess longitudinal bone growth and body weight was monitored throughout the study. Histomorphometric and immunohistochemical analyses were performed to evaluate treatment effects on the growth plate cartilage. Venetoclax decreased the viability of chondrocytes and impaired the growth of ex vivo cultured metatarsals while reducing the height of the resting/proliferative zone and the hypertrophic cell size. When tested in vivo, venetoclax suppressed bone growth and reduced growth plate height. Our experimental data suggest that venetoclax directly targets growth plate chondrocytes suppressing bone growth and we, therefore, encourage careful monitoring of longitudinal bone growth if treating growing children with venetoclax.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Humanin Treatment Protects Against Venetoclax-Induced Bone Growth Retardation in Ex Vivo Cultured Rat Bones.J Endocr Soc. 2024 Jan 25;8(3):bvae009. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvae009. eCollection 2024 Jan 16. J Endocr Soc. 2024. PMID: 38328478 Free PMC article.
-
Bortezomib is cytotoxic to the human growth plate and permanently impairs bone growth in young mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50523. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050523. Epub 2012 Nov 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23226303 Free PMC article.
-
Fluoride Inhibits Longitudinal Bone Growth by Acting Directly at the Growth Plate in Cultured Neonatal Rat Metatarsal Bones.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020 Oct;197(2):522-532. doi: 10.1007/s12011-019-01997-9. Epub 2019 Dec 14. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020. PMID: 31838736
-
Matrix metalloproteinases: role in skeletal development and growth plate disorders.Front Biosci. 2006 May 1;11:1702-15. doi: 10.2741/1916. Front Biosci. 2006. PMID: 16368549 Review.
-
Local regulation of growth plate cartilage.Endocr Dev. 2011;21:12-22. doi: 10.1159/000328084. Epub 2011 Aug 22. Endocr Dev. 2011. PMID: 21865750 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent development of mitochondrial metabolism and dysfunction in osteoarthritis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 13;16:1538662. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1538662. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40017603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Network Pharmacology and Molecular Modeling Techniques in Unraveling the Underlying Mechanism of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium aganist Type 2 Diabetic Osteoporosis.Nutrients. 2024 Jan 10;16(2):220. doi: 10.3390/nu16020220. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38257113 Free PMC article.
-
Humanin Treatment Protects Against Venetoclax-Induced Bone Growth Retardation in Ex Vivo Cultured Rat Bones.J Endocr Soc. 2024 Jan 25;8(3):bvae009. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvae009. eCollection 2024 Jan 16. J Endocr Soc. 2024. PMID: 38328478 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

