The effect of sulfur baths on hemorheological properties of blood in patients with osteoarthritis
- PMID: 37198390
- PMCID: PMC10192410
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-35264-8
The effect of sulfur baths on hemorheological properties of blood in patients with osteoarthritis
Abstract
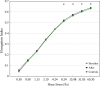
Balneotherapy is an effective treatment method in various diseases and commonly used treatment modality among patients with musculoskeletal disorders. Sulfur baths are known for healing properties however effect on rheological properties is unstudied. Thus the aim of our study was to determine the effect of sulfur balneotherapy on hemorheological blood indices. A total of 48 patients with osteoarthritis were enrolled to the study. Blood samples were collected twice, before and after 3-week time period. We evaluated complete blood count, fibrinogen, hs-CRP and blood rheology parameters such as elongation index (EI), half-time of total aggregation (T1/2) and aggregation index (AI) analyzed with the Lorrca Maxis. Mean age of studied cohort was 67 ± 5 years. After sulfur baths WBC count was significantly decreased is studied group (p = 0.021) as well as neutrophile count (p = 0.036). Red blood cell EIs were statistically higher after sulfur baths in shear stress ranging from 8.24 to 60.30 Pa. T1/2 was significantly higher (p = 0.031) and AI lower (p = 0.003) compared to baseline. No significant changes in fibrinogen and hs-CRP were observed. It is the first study that evaluate effect of sulfur balneotherapy on rheologic properties of blood. Sulfur water baths may improve erythrocyte deformability and aggregation parameters.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Legwant Z, Gawęda J, Legwant-Wójcicka M, Kornecki W. Evaluation of comprehensive spa treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee at the “Włókniarz” sanatorium in Busko-Zdrój. Med. Stud. Med. 2013;29:167–170. doi: 10.5114/ms.2013.36887. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous