PET/CT reading for relapse in non-small cell lung cancer after chemoradiotherapy in the PET-Plan trial cohort
- PMID: 37198668
- PMCID: PMC10190104
- DOI: 10.1186/s40644-023-00567-6
PET/CT reading for relapse in non-small cell lung cancer after chemoradiotherapy in the PET-Plan trial cohort
Abstract
Background: Current studies indicate that fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/ computed tomography ([18F]FDG PET/CT) is the most accurate imaging modality for the detection of relapsed locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) after curatively intended chemoradiotherapy. To this day, there is no objective and reproducible definition for the diagnosis of disease recurrence in PET/CT, the reading of which is relevantly influenced by post radiation inflammatory processes. The aim of this study was to evaluate and compare visual and threshold-based semi-automated evaluation criteria for the assessment of suspected tumor recurrence in a well-defined study population investigated during the randomized clinical PET-Plan trial.
Methods: This retrospective analysis comprises 114 PET/CT data sets of 82 patients from the PET-Plan multi-center study cohort who underwent [18F]FDG PET/CT imaging at different timepoints for relapse, as suspected by CT. Scans were first analyzed visually by four blinded readers using a binary scoring system for each possible localization and the associated reader certainty of the evaluation. Visual evaluations were conducted repeatedly without and with additional knowledge of the initial staging PET and radiotherapy delineation volumes. In a second step, uptake was measured quantitatively using maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax), peak standardized uptake value corrected for lean body mass (SULpeak), and a liver threshold-based quantitative assessment model. Resulting sensitivity and specificity for relapse detection were compared to the findings in the visual assessment. The gold standard of recurrence was independently defined by prospective study routine including external reviewers using CT, PET, biopsies and clinical course of the disease.
Results: Overall interobserver agreement (IOA) of the visual assessment was moderate with a high difference between secure (ĸ = 0.66) and insecure (ĸ = 0.24) evaluations. Additional knowledge of the initial staging PET and radiotherapy delineation volumes improved the sensitivity (0.85 vs 0.92) but did not show significant impact on the specificity (0.86 vs 0.89). PET parameters SUVmax and SULpeak showed lower accuracy compared to the visual assessment, whereas threshold-based reading showed similar sensitivity (0.86) and higher specificity (0.97).
Conclusion: Visual assessment especially if associated with high reader certainty shows very high interobserver agreement and high accuracy that can be further increased by baseline PET/CT information. The implementation of a patient individual liver threshold value definition, similar to the threshold definition in PERCIST, offers a more standardized method matching the accuracy of experienced readers albeit not providing further improvement of accuracy.
Keywords: NSCLC; Oncology; PET/CT; Relapse criteria; Tumor recurrence.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
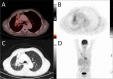
References
-
- van Tinteren H, Hoekstra OS, Smit EF, van den Bergh JH, Schreurs AJ, Stallaert RA, van Velthoven PC, Comans EF, Diepenhorst FW, Verboom P, et al. Effectiveness of positron emission tomography in the preoperative assessment of patients with suspected non-small-cell lung cancer: the PLUS multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2002;359(9315):1388–1393. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)08352-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- MacManus MP, Hicks RJ, Matthews JP, Hogg A, McKenzie AF, Wirth A, Ware RE, Ball DL. High rate of detection of unsuspected distant metastases by pet in apparent stage III non-small-cell lung cancer: implications for radical radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001;50(2):287–293. doi: 10.1016/S0360-3016(01)01477-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

