Multidrug resistant 1 (MDR1) C3435T and G2677T gene polymorphism: impact on the risk of acute rejection in pediatric kidney transplant recipients
- PMID: 37198710
- PMCID: PMC10193607
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-023-01469-w
Multidrug resistant 1 (MDR1) C3435T and G2677T gene polymorphism: impact on the risk of acute rejection in pediatric kidney transplant recipients
Abstract
Background: Tacrolimus is the backbone drug in kidney transplantation. Single nucleotide polymorphism of Multidrug resistant 1 gene can affect tacrolimus metabolism consequently it can affect tacrolimus trough level and incidence of acute rejection. The aim of this study is to investigate the impact of Multidrug resistant 1 gene, C3435T and G2677T Single nucleotide polymorphisms on tacrolimus pharmacokinetics and on the risk of acute rejection in pediatric kidney transplant recipients.
Methods: Typing of Multidrug resistant 1 gene, C3435T and G2677T gene polymorphism was done using polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) for 83 pediatric kidney transplant recipients and 80 matched healthy controls.
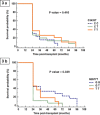
Results: In Multidrug resistant 1 gene (C3435T), CC, CT genotypes and C allele were significantly associated with risk of acute rejection when compared to none acute rejection group (P = 0.008, 0.001 and 0.01 respectively). The required tacrolimus doses to achieve trough level were significantly higher among CC than CT than TT genotypes through the 1st 6 months after kidney transplantation. While, in Multidrug resistant 1 gene (G2677T), GT, TT genotypes and T allele were associated with acute rejection when compared to none acute rejection (P = 0.023, 0.033 and 0.028 respectively). The required tacrolimus doses to achieve trough level were significantly higher among TT than GT than GG genotypes through the 1st 6 months after kidney transplantation.
Conclusion: The C allele, CC and CT genotypes of Multidrug resistant 1 gene (C3435T) and the T allele, GT and TT genotypes of Multidrug resistant 1 gene (G2677T) gene polymorphism may be risk factors for acute rejection and this can be attributed to their effect on tacrolimus pharmacokinetics. Tacrolimus therapy may be tailored according to the recipient genotype for better outcome.
Keywords: Acute rejection; Kidney transplantation; Multidrug resistant 1 gene; Tacrolimus pharmacokinetics.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of CYP3A5, ABCB1, and CYP2C8 Polymorphisms with Renal Function in Kidney Transplant Recipients Receiving Tacrolimus.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2025 Sep;50(5):383-397. doi: 10.1007/s13318-025-00955-2. Epub 2025 Jul 1. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2025. PMID: 40591133
-
The effect of CYP3A4, CYP3A5 and MDR1 (ABCB1) single nucleotide polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of cyclosporine in Algerian stable renal transplant recipients.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jul 25;52(1):756. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10862-z. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40711648
-
Sex and gender as predictors for allograft and patient-relevant outcomes after kidney transplantation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 19;12(12):CD014966. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014966.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39698949
-
Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies for treating acute rejection episodes in kidney transplant recipients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 20;7(7):CD004756. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004756.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28731207 Free PMC article.
-
Belatacept for kidney transplant recipients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Nov 24;2014(11):CD010699. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010699.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25416857 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pharmacogenetics association with long-term clinical evolution in a kidney transplant patients cohort.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2025 Jul 24;9:100230. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2025.100230. eCollection 2025. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2025. PMID: 40761554 Free PMC article.
-
A descriptive study of the single-nucleotide polymorphisms known to affect the Tacrolimus trough concentration per dose, among a population of kidney failure patients in a tertiary hospital in Ghana.BMC Res Notes. 2024 Jul 29;17(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s13104-024-06868-8. BMC Res Notes. 2024. PMID: 39080672 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allain-Launay E, Roussey‐Kesler G, Ranchin B, Guest G, Maisin A, Novo R et al. Mortality in pediatric renal transplantation: a study of the French pediatric kidney database. Pediatric transplantation. 2009;13(6):725 –30. 10.1111/j.1399-3046.2009.01036.x. PMID: 19691564. - PubMed
-
- Kamali K, Abbasi MA, Farokhi B, Abbasi A, Fallah P, Seifee MH, et al. Posttransplant soluble CD30 as a predictor of acute renal allograft rejection. Exp Clin Transplant. 2009;7(4):237. - PubMed
-
- Naik RH, Shawar SH. Renal transplantation rejection. StatPearls. 2020. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous