Safety and Efficacy of Cortical Bone Trajectory Screw Fixation Combined with Facet Fusion for the Treatment of Lumbar Degenerative Disease
- PMID: 37199023
- PMCID: PMC10235161
- DOI: 10.1111/os.13752
Safety and Efficacy of Cortical Bone Trajectory Screw Fixation Combined with Facet Fusion for the Treatment of Lumbar Degenerative Disease
Abstract
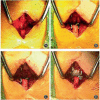
Objective: The mainstream lumbar fusion surgeries have various shortcomings, such as complex operation, much invasion, and loss of lumbar function. How to minimize the surgical injury and to achieve better therapeutic effects has become the goal pursued by spine surgeons. This study introduces a cortical bone trajectory (CBT) screw fixation combined with facet fusion (FF), evaluates its safety and efficacy, and explores its advantages, in order to provide a reference for treatment of patients with single-level lumbar stenosis or grade I degenerative spondylolisthesis.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the clinical, radiological, and operative data of 167 patients with single-level lumbar stenosis or grade I degenerative spondylolisthesis who underwent FF or transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) from January 2013 to September 2019 in the spine surgery department of the Second Hospital of Shandong University. Patients were divided into four groups according to surgical method: group CBT-FF, CBT screw combined with FF; group PS-FF, pedicle screw (PS) combined with FF; group CBT-TLIF, CBT screw combined with TLIF; and group PS-TLIF, PS combined with TLIF. The operation time, estimated intraoperative blood loss, complications after surgery, visual analog scale (VAS), and Oswestry disability index (ODI) of the four groups were compared. The fusion was evaluated by anteroposterior and lateral X-ray, CT scan, and three-dimensional reconstruction.
Results: Twelve months after surgery, the fusion rate of four groups had no significantly statistical differences (p = 0.914). VAS and ODI scores were lower after surgery than before. Low back pain VAS scores 1 week after surgery in group CBT-FF and group CBT-TLIF were significantly lower than those in group PS-FF and group PS-TLIF (pCF/PF = 0.001, pCF/PT = 0.000, pPF/CT = 0.049, pCT/PT = 0.000). Low back pain VAS score 3 months after surgery was significantly lower in group CBT-FF than group PS-FF and group PS-TLIF (pCF/PF = 0.045, pCF/PT = 0.008). ODI score 1 week after surgery was significantly lower in group CBT-FF than group PS-FF, group CBT-TLIF, and group PS-TLIF (pCF/PF = 0.000, pCF/CT = 0.005, pCF/PT = 0.000, pCT/PT = 0.015). ODI score 3 months after surgery was significantly lower in group CBT-FF than group PS-FF, group CBT-TLIF, and group PS-TLIF (pCF/PF = 0.001, pCF/CT = 0.002, pCF/PT = 0.000). Incidence of complications did not significantly differ among the groups.
Conclusion: CBT screw fixation combined with FF is a safe and efficacious procedure for patients with single-level lumbar stenosis or grade I degenerative spondylolisthesis. This minimally invasive approach of lumbar fusion can be simply and easily performed. Patients who undergo CBT screw fixation combined with FF recovered faster than TLIF.
Keywords: Cortical Bone Trajectory Screw; Facet Fusion; Lumbar Degenerative Disorders; Pedicle Screw; Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion.
© 2023 The Authors. Orthopaedic Surgery published by Tianjin Hospital and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with cortical bone trajectory screw fixation versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion using traditional pedicle screw fixation for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: a comparative study.J Neurosurg Spine. 2016 Nov;25(5):591-595. doi: 10.3171/2016.3.SPINE151525. Epub 2016 May 27. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016. PMID: 27231813
-
Percutaneous Endoscopic Robot-Assisted Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PE RA-TLIF) for Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: A Technical Note and Two Years Clinical Results.Pain Physician. 2022 Jan;25(1):E73-E86. Pain Physician. 2022. PMID: 35051154
-
Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with cortical bone trajectory screws versus traditional pedicle screws fixation: a study protocol of randomised controlled trial.BMJ Open. 2017 Oct 22;7(10):e017227. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-017227. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 29061616 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative clinical efficacy and safety of cortical bone trajectory screw fixation and traditional pedicle screw fixation in posterior lumbar fusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Spine J. 2019 Jul;28(7):1678-1689. doi: 10.1007/s00586-019-05999-y. Epub 2019 May 13. Eur Spine J. 2019. PMID: 31087165
-
Comparative effectiveness of cortical bone trajectory screws and pedicle screws in the treatment of adjacent segment degeneration after lumbar fusion surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Jun 28;19(1):380. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04865-y. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 38943143 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Enhancing Low Back Pain Management: The Diagnostic and Prognostic Role of Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography-Computerized Tomography (SPECT-CT) in Surgical Outcomes.Cureus. 2025 May 13;17(5):e84015. doi: 10.7759/cureus.84015. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40510094 Free PMC article.
-
[Effectiveness of robot-assisted minimally invasive and open freehand transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in treatment of single-level degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis and the influence on adjacent segment degeneration].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Nov 15;38(11):1379-1385. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202404059. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39542631 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- McAnany SJ, Baird EO, Qureshi SA, Hecht AC, Heller JG, Anderson PA. Posterolateral fusion versus interbody fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Spine. 2016;41(23):E1408–e14. - PubMed
-
- Kim HS, Wu PH, Jang IT. Lumbar degenerative disease part 1: anatomy and pathophysiology of intervertebral Discogenic pain and radiofrequency ablation of Basivertebral and Sinuvertebral nerve treatment for chronic Discogenic Back pain: a prospective case series and review of literature. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(4):1483. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gibson JN, Waddell G. Surgery for degenerative lumbar spondylosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005;30(20):2312–20. - PubMed
-
- Makanji H, Schoenfeld AJ, Bhalla A, Bono CM. Critical analysis of trends in lumbar fusion for degenerative disorders revisited: influence of technique on fusion rate and clinical outcomes. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(8):1868–76. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

