Exosomal MicroRNA-223, MicroRNA-146, and MicroRNA-21 Profiles and Biochemical Changes in Laryngeal Cancer
- PMID: 37200807
- PMCID: PMC10186621
- DOI: 10.1021/acsptsci.3c00038
Exosomal MicroRNA-223, MicroRNA-146, and MicroRNA-21 Profiles and Biochemical Changes in Laryngeal Cancer
Abstract
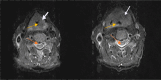
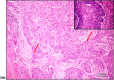
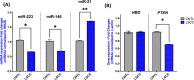
Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) is one of the most aggressive cancers, and its early diagnosis is urgent. Exosomes are believed to have diagnostic significance in cancer. However, the role of serum exosomal microRNAs, miR-223, miR-146, and miR-21, and phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) and hemoglobin subunit delta (HBD) mRNAs in LSCC is unclear. Exosomes were isolated from the blood serum of 10 LSCC patients and 10 healthy controls to perform scanning electron microscopy and liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry analyses to characterize them and to undergo reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction to identify miR-223, miR-146, miR-21, and PTEN and HBD mRNA expression phenotypes. Biochemical parameters, including serum C-reactive protein (CRP) and vitamin B12, were also obtained. Serum exosomes of 10-140 nm were isolated from LSCC and controls. Serum exosomal miR-223, miR-146, and PTEN were found to be significantly decreased (p < 0.05), in contrast to serum exosomal miRNA-21 (p < 0.01), and serum vitamin B12 and CRP (p < 0.05) were found to be significantly increased, in LSCC vs controls. Our novel data show that the combination of reduced serum exosomal miR-223, miR-146, and miR-21 profiles and biochemical alterations in CRP and vitamin B12 levels may be useful indicators of LSCC that could be validated by large studies. Our findings also suggest a possible negative regulatory effect of miR-21 on PTEN in LSCC, encouraging a more extensive investigation of its role.
© 2023 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Combined detection of serum exosomal miR-21 and HOTAIR as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Med Oncol. 2014 Sep;31(9):148. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0148-8. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Med Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25099764
-
MicroRNA 744-3p promotes MMP-9-mediated metastasis by simultaneously suppressing PDCD4 and PTEN in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 6;7(36):58218-58233. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11280. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27533461 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Exosomal miR-941 as a promising Oncogenic Biomarker for Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.J Cancer. 2020 Jul 9;11(18):5329-5344. doi: 10.7150/jca.45394. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32742479 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Exosomal MicroRNA-21, MicroRNA-126, and PTEN Are Novel Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Acute Coronary Syndrome.Front Physiol. 2020 Jun 11;11:654. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00654. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32595526 Free PMC article.
-
Serum expression of selected miRNAs in patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC).Diagn Pathol. 2019 May 28;14(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s13000-019-0823-3. Diagn Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31138255 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
MiR-29 and MiR-140 regulate TRAIL-induced drug tolerance in lung cancer.Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2024 Apr 30;28(1):184-197. doi: 10.1080/19768354.2024.2345644. eCollection 2024. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2024. PMID: 38693921 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring salivary exosomes as early predictors of oral cancer in susceptible tobacco consumers: noninvasive diagnostic and prognostic applications.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Nov;149(17):15781-15793. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05343-4. Epub 2023 Sep 5. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37668794 Free PMC article.
-
Free circulating versus extracellular vesicle-associated microRNA expression in canine T-cell lymphoma.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Aug 29;11:1461506. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1461506. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39268522 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
