Sirt1 protects against intervertebral disc degeneration induced by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D insufficiency in mice by inhibiting the NF-κB inflammatory pathway
- PMID: 37200907
- PMCID: PMC10185703
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jot.2023.04.003
Sirt1 protects against intervertebral disc degeneration induced by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D insufficiency in mice by inhibiting the NF-κB inflammatory pathway
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Sirt1 protects against intervertebral disc degeneration induced by 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D insufficiency in mice by inhibiting the NF-κB inflammatory pathway"[Journal of Orthopaedic Translation 40 (2023) 13-26].J Orthop Translat. 2024 Sep 3;48:247-253. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2024.08.019. eCollection 2024 Sep. J Orthop Translat. 2024. PMID: 40224509 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: It has been demonstrated that vitamin D deficiency is associated with an increased risk of patients developing lumbar disc herniation. However, intervertebral disc degeneration caused by active vitamin D deficiency has not been reported. Thus, the purpose of this study was to e investigate the role and mechanism of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25(OH)2D) insufficiency in promoting intervertebral disc degeneration.
Methods: The phenotypes of intervertebral discs were compared in wild-type mice and mice with heterozygous deletion of 1α-hydroxylase [1α(OH)ase+/-] at 8 mouths of age using iconography, histology and molecular biology. A mouse model that overexpressed Sirt1 in mesenchymal stem cells on a 1α(OH)ase+/- background (Sirt1Tg/1α(OH)ase+/-) was generated by crossing Prx1-Sirt1 transgenic mice with 1α(OH)ase+/- mice and comparing their intervertebral disc phenotypes with those of Sirt1Tg, 1α(OH)ase+/- and wild-type littermates at 8 months of age. A vitamin D receptor (VDR)-deficient cellular model was generated by knock-down of endogenous VDR using Ad-siVDR transfection into nucleus pulposus cells; VDR-deficient nucleus pulposus cells were then treated with or without resveratrol. The interactions between Sirt1 and acetylated p65, and p65 nuclear localization, were examined using co-immunoprecipitation, Western blots and immunofluorescence staining. VDR-deficient nucleus pulposus cells were also treated with 1,25(OH)2D3, or resveratrol or 1,25(OH)2D3 plus Ex527 (an inhibitor of Sirt1). Effects on Sirt1 expression, cell proliferation, cell senescence, extracellular matrix protein synthesis and degradation, nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), and expression of inflammatory molecules, were examined, using immunofluorescence staining, Western blots and real-time RT-PCR.
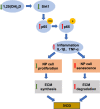
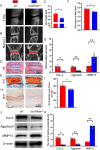
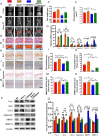
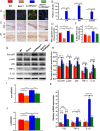
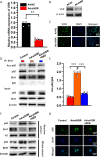
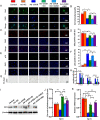
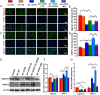
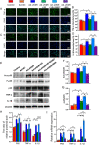
Results: 1,25(OH)2D insufficiency accelerated intervertebral disc degeneration by reducing extracellular matrix protein synthesis and enhancing extracellular matrix protein degradation with reduced Sirt1 expression in nucleus pulposus tissues. Overexpression of Sirt1 in MSCs protected against 1,25(OH)2D deficiency-induced intervertebral disc degeneration by decreasing acetylation and phosphorylation of p65 and inhibiting the NF-κB inflammatory pathway. VDR or resveratrol activated Sirt1 to deacetylate p65 and inhibit its nuclear translocation into nucleus pulposus cells. Knockdown of VDR decreased VDR expression and significantly reduced the proliferation and extracellular matrix protein synthesis of nucleus pulposus cells, significantly increased the senescence of nucleus pulposus cells and significantly downregulated Sirt1 expression, and upregulated matrix metallopeptidase 13 (MMP13), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin 1β (IL-1β) expression; the ratios of acetylated and phosphorylated p65/p65 in nucleus pulposus cells were also increased. Treatment of nucleus pulposus cells with VDR reduction using 1,25(OH)2D3 or resveratrol partially rescued the degeneration phenotypes, by up-regulating Sirt1 expression and inhibiting NF-κB inflammatory pathway; these effects in nucleus pulposus cells were blocked by inhibition of Sirt1.
Conclusion: Results from this study indicate that the 1,25(OH)2D/VDR pathway can prevent the degeneration of nucleus pulposus cells by inhibiting the NF-κB inflammatory pathway mediated by Sirt1.The Translational Potential of This Article: This study provides new insights into the use of 1,25(OH)2D3 to prevent and treat intervertebral disc degeneration caused by vitamin D deficiency.
Keywords: Intervertebral disc degeneration; NF-κB; Sirt1; Vitamin D; Vitamin D receptor.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ZNF667 alleviates the inflammatory damage in intervertebral disc degeneration via inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Oct 28;49(10):1611-1621. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.240122. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 40074310 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D Deficiency Accelerates Aging-related Osteoarthritis via Downregulation of Sirt1 in Mice.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Jan 1;19(2):610-624. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.78785. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36632467 Free PMC article.
-
[Expression of NF-κB in a degenerative human intervertebral disc model].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017 May 9;97(17):1324-1329. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2017.17.011. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28482435 Chinese.
-
[Resveratrol regulate the extracellular matrix expression via Wnt/β-catenin pathway in nucleus pulposus cells].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Apr 15;32(4):476-483. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201709097. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29806307 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Innovating intervertebral disc degeneration therapy: Harnessing the power of extracellular vesicles.J Orthop Translat. 2025 Jan 7;50:44-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2024.09.014. eCollection 2025 Jan. J Orthop Translat. 2025. PMID: 39868351 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of micronutrients and serum metabolites in intervertebral disk degeneration: insights from a Mendelian randomization study and mediation analysis.Front Nutr. 2024 Oct 21;11:1428403. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1428403. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39498405 Free PMC article.
-
Innovation and Translation of Biological and Biomaterial Treatment for Challenging Musculoskeletal Disorders.J Orthop Translat. 2023 Jun 29;40:A1. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2023.06.001. eCollection 2023 May. J Orthop Translat. 2023. PMID: 37457312 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Nrf2 activation by pyrroloquinoline quinone inhibits natural aging-related intervertebral disk degeneration in mice.Aging Cell. 2024 Aug;23(8):e14202. doi: 10.1111/acel.14202. Epub 2024 May 23. Aging Cell. 2024. PMID: 38780001 Free PMC article.
-
Natural products for intervertebral disc degeneration: mechanistic insights and therapeutic potentials.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 25;16:1605764. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1605764. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40786036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-specific Sirt1 overexpression prevents sarcopenia induced by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D deficiency.Aging (Albany NY). 2025 Mar 31;17(4):1026-1042. doi: 10.18632/aging.206232. Epub 2025 Mar 31. Aging (Albany NY). 2025. PMID: 40168539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tiosano D., Gepstein V. Vitamin D action: lessons learned from hereditary 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin-D-resistant rickets patients. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2012;19(6):452–459. - PubMed
-
- Grubler M.R., Gangler S., Egli A., Bischoff-Ferrari H.A. Effects of vitamin D3 on glucose metabolism in patients with severe osteoarthritis: a randomized double-blind trial comparing daily 2000 with 800 IU vitamin D3. Diabetes Obes Metabol. 2021;23(4):1011–1019. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

