'CROSS'-ing into the 'Real World': a retrospective cohort study of patients receiving trimodality and bimodality therapy for esophageal cancer
- PMID: 37201058
- PMCID: PMC10186498
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-22-633
'CROSS'-ing into the 'Real World': a retrospective cohort study of patients receiving trimodality and bimodality therapy for esophageal cancer
Abstract
Background: A standard of care for nonmetastatic esophageal cancer is trimodality therapy consisting of neoadjuvant chemoradiation and esophagectomy, with evidence for improved overall survival versus surgery alone in the ChemoRadiotherapy for Oesophageal cancer followed by Surgery Study (CROSS) trial. Patients who receive treatment with curative intent but are poor candidates for or decline surgery receive definitive bimodality therapy. Literature characterizing patients who receive bimodality therapy compared to trimodality therapy, and their relative outcomes, is sparse, especially among patients who are too old or too frail to qualify for clinical trials. In this study, we assess a single-institution real-world dataset of patients receiving bimodality and trimodality management.
Methods: Patients treated for clinically resectable, nonmetastatic esophageal cancer between 2009 and 2019 who received bimodality or trimodality therapy were reviewed, generating a dataset of 95 patients. Clinical variables and patient characteristics were assessed for association with modality on multivariable logistic regression. Overall, relapse-free, and disease-free survival were assessed with Kaplan-Meier analyses and Cox proportional modeling. For patients nonadherent to planned esophagectomy, reasons for nonadherence were recorded.
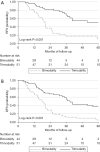
Results: Bimodality therapy was associated with greater age-adjusted comorbidity index, worse performance status, higher N-stage, presenting symptom other than dysphagia, and held chemotherapy cycles on multivariable analysis. Compared to bimodality therapy, trimodality therapy was associated with higher overall (3-year: 62% vs. 18%, P<0.001), relapse-free (3-year: 71% vs. 18%, P<0.001), and disease-free (3-year: 58% vs. 12%, P<0.001) survival. Similar results were observed among patients who did not meet CROSS trial qualifying criteria. Only treatment modality was associated with overall survival after adjusting for covariates (HR 0.37, P<0.001, reference group: bimodality). Patient choice accounted for 40% of surgery nonadherence in our population.
Conclusions: Patients receiving trimodality therapy were observed to have superior overall survival compared to bimodality therapy. Patient preference for organ-preserving therapies appears to impact resection rate; further characterization of patient decision-making may be helpful. Our results suggest patients who wish to prioritize overall survival should be encouraged to pursue trimodality therapy and obtain early consultation with surgery. Development of evidence-based interventions to physiologically prepare patients before and during neoadjuvant therapy as well as efforts to optimize the tolerability of the chemoradiation plan are warranted.
Keywords: Esophageal neoplasms; esophagectomy; neoadjuvant therapy.
2023 Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jgo.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jgo-22-633/coif). All authors report that this study received financial support from NNECOS and the UVM LCOM Summer Research Fellowship. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect those of the NNECOS. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Anker CJ, Dragovic J, Herman JM, et al. Executive Summary of the American Radium Society Appropriate Use Criteria for Operable Esophageal and Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma: Systematic Review and Guidelines. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2021;109:186-200. 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.08.050 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
