Exosomal miR-125b-5p derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes the growth, migration, and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells by decreasing adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) expression
- PMID: 37201069
- PMCID: PMC10186528
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-23-198
Exosomal miR-125b-5p derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes the growth, migration, and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells by decreasing adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) expression
Abstract
Background: A significant desmoplastic response, particularly in the fibroblasts, is a characteristic of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Increasing evidence has shown that cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) assist tumor development, invasion, and metastasis in PDAC. However, CAFs-derived molecular determinants that regulate the molecular mechanisms of PDAC have not been fully characterized.
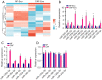
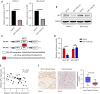
Methods: The expression of microRNA 125b-5p (miR-125b-5p) in Pancreas Cancer (PC) tissue and para-cancerous normal tissue was examined using Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Cell counting kit-8 (CCK8), wound healing, and transwell experiments were utilized to assess the effect of miR-125b-5p. Using a cell luciferase activity test and bioinformatics, it was demonstrated that miR-125b-5p may bind to the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), thereby limiting the progression of pancreatic cancer.
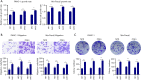
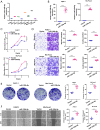
Results: PDAC cells are prompted to proliferate, undergo the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and spread. Importantly, CAFs release exosomes into PDAC cells, which significantly increase the level of miR-125b-5p in those cells. Meanwhile, pancreatic cancer cell lines and PDAC tissues have considerably higher miR-125b-5p expression. MiR-125b-5p's elevated expression mechanically suppresses the expression of APC and accelerates the spread of pancreatic cancer.
Conclusions: Exosomes released by CAFs promote PDAC growth, invasion, and metastasis. Exosomal miR-125b-5p inhibition offers an alternate strategy for combating the basic malady of PDAC.
Keywords: Pancreatic cancer; adenomatous polyposis coli (APC); cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs); exosomes; miR-125b-5p.
2023 Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jgo.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jgo-23-198/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Bejarano L, Jordao MJC, Joyce JA. Therapeutic Targeting of the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Discov 2021;11:933-59. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1808 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
