Identification of glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase as a new therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma via a novel bioinformatic approach
- PMID: 37201074
- PMCID: PMC10186547
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-23-247
Identification of glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase as a new therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma via a novel bioinformatic approach
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has a high incidence, and current treatments are ineffective. We aimed to explore potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for HCC by conducting bioinformatics analysis on genomic and proteomic data.
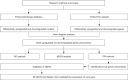
Methods: Genome and proteome data were downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and ProteomeXchange databases, respectively. Differentially expressed genes was determined using limma package. Functional enrichment analysis was conducted by Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery (DAVID). Protein-protein analysis was established by STRING dataset. Using Cytoscope for network visualization and CytoHubba for hub gene identification. The gene mRNA and protein levels were validated using GEPIA and HPA, as well as RT-qPCR and Western blot.
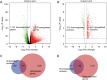
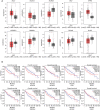
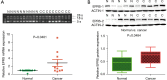
Results: A total of 127 up-regulated and 80 down-regulated common DEGPs were identified between the genomic and proteomic data, Mining 10 key genes/proteins(ACLY, ACACB, EPRS, CAD, HSPA4, ACACA, MTHFD1, DMGDH, ALDH2, and GLDC) through protein interaction networks. in addition, Glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase (EPRS) was highlighted as an HCC biomarker that is negatively correlated with survival. Differential EPRS expression analysis in HCC and paracancerous tissues showed that EPRS expression was elevated in HCC. RT-qPCR and Western blot analysis results showed that EPRS expression was upregulated in HCC cells.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that EPRS is a potential therapeutic target for inhibiting HCC tumorigenesis and progression.
Keywords: ATP citrate lyase (ACLY); ProteomeXchange; The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA); glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase (EPRS); heat shock protein family A member 4 (HSPA4).
2023 Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jgo.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jgo-23-247/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
