Genomic Determinants of Pathogenicity and Antimicrobial Resistance of Nosocomial Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates of Hospitalized Patients (2019-2021) from a Sentinel Hospital in Hangzhou, China
- PMID: 37201122
- PMCID: PMC10187652
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S407577
Genomic Determinants of Pathogenicity and Antimicrobial Resistance of Nosocomial Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates of Hospitalized Patients (2019-2021) from a Sentinel Hospital in Hangzhou, China
Abstract
Purpose: Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii or AB) is one of the most opportunistic, nosocomial pathogens threatening public healthcare across countries. A. baumannii has become a primary growing concern due to its exceptional ability to acquire antimicrobial resistance (AMR) to multiple antimicrobial agents which is increasingly reported and more prevalent every year. Therefore, there is an urgent need to evaluate the AMR knowledge of A. baumannii for effective clinical treatment of nosocomial infections. This study aimed to investigate the clinical distribution AMR phenotypes and genotypes, and genomic characteristics of A. baumannii isolates recovered from hospitalized patients of different clinical departments of a sentinel hospital to improve clinical practices.
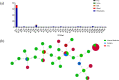
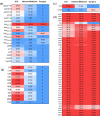
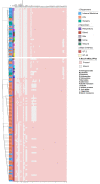
Methods: A total of 123 clinical isolates were recovered from hospitalized patients of different clinical departments during 2019-2021 to analyze AMR patterns, and further subjected to whole-genome sequencing (WGS) investigations. Multi-locus sequence typing (MLST), as well as the presence of antimicrobial-resistant genes (ARGs), virulence factor genes (VFGs) and insertion sequences (ISs) were also investigated from WGS data.
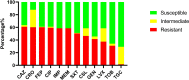
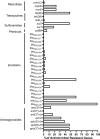
Results: The results highlighted that A. baumannii clinical isolates had shown a high AMR rate, particularly from the intensive care unit (ICU), towards routinely used antimicrobials, ie, β-lactams and fluoroquinolones. ST2 was the most prevalent ST in the clinical isolates, it was strongly associated to the resistance of cephalosporins and carbapenems, with blaOXA-23 and blaOXA-66 being the most frequent determinants; moreover, high carrier rate of VFGs was also observed such as all strains containing the ompA, adeF, pgaC, lpsB, and bfmR genes.
Conclusion: Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates are mostly ST2 with high rates of drug resistance and carrier of virulence factors. Therefore, it requires measurements to control its transmission and infection.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; antimicrobial resistance; genetic determinants; virulence factors; whole-genome sequencing.
© 2023 Wei et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular Epidemiology and Genetic Characterization of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates from the ICU of a Tertiary Hospital in East China.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Dec 31;17:5925-5945. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S491858. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39759767 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic and WGS-derived antimicrobial resistance profiles of clinical and non-clinical Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from Germany and Vietnam.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020 Oct;56(4):106127. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106127. Epub 2020 Aug 1. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020. PMID: 32750418
-
Phenotypic and molecular characterization of Acinetobacter baumannii isolates causing lower respiratory infections among ICU patients.Microb Pathog. 2019 Mar;128:75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.12.023. Epub 2018 Dec 15. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30562602
-
Acinetobacter spp. as nosocomial pathogens: Epidemiology and resistance features.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018 Mar;25(3):586-596. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2016.02.009. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29686523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pan-Genome Plasticity and Virulence Factors: A Natural Treasure Trove for Acinetobacter baumannii.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Mar 14;13(3):257. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13030257. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38534692 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Genome Analysis of Colistin-Only-Sensitive KPC-2 and NDM1-1-Coproducing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 and Acinetobacter baumannii ST2 From a Critically Ill Patient With COVID-19 in Saudi Arabia: Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) of K. pneumoniae ST11 and A. baumannii ST2.Int J Microbiol. 2024 Oct 29;2024:9233075. doi: 10.1155/2024/9233075. eCollection 2024. Int J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39502515 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Raman spectroscopy with mass spectrometry for sequence typing of Acinetobacter baumannii strains: a single-center study.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Mar 4;13(3):e0142524. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01425-24. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 39907463 Free PMC article.
-
Research and predictive analysis of the disease burden of bloodstream infectious diseases in China.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Apr 22;25(1):578. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10989-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40264014 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome sequencing of Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates from a tertiary hospital in Terengganu, Malaysia (2011-2020), revealed the predominance of the Global Clone 2 lineage.Microb Genom. 2025 Feb;11(2):001345. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.001345. Microb Genom. 2025. PMID: 39908088 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning and feature extraction for rapid antimicrobial resistance prediction of Acinetobacter baumannii from whole-genome sequencing data.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jan 11;14:1320312. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1320312. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38274740 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martin-Aspas A, Guerrero-Sanchez FM, Garcia-Colchero F, Rodriguez-Roca S, Giron-Gonzalez JA. Differential characteristics of Acinetobacter baumannii colonization and infection: risk factors, clinical picture, and mortality. Infect Drug Resist. 2018;11:861–872. doi:10.2147/IDR.S163944 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

