Efficacy of modified thoracoabdominal nerve block through perichondrial approach following laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair surgery: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 37201747
- PMCID: PMC10533976
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjane.2023.05.001
Efficacy of modified thoracoabdominal nerve block through perichondrial approach following laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair surgery: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
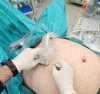
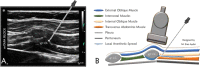
Background: Modified thoracoabdominal nerve block through perichondrial approach is a novel fascial plane block and provides abdominal analgesia by blocking thoracoabdominal nerves. Our primary aim was to evaluate the efficacy of M-TAPA on quality of recovery and pain scores in patients who underwent laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair surgery (Trans Abdominal Pre-Peritoneal approach ‒ TAPP).
Methods: Patients with American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) physical status I-II aged between 18 and 65 years scheduled for elective TAPP under general anesthesia were enrolled in the study. After intubation, the patients were randomized into two groups: M: M-TAPA group (n = 30) and the control group (n = 30). M-TAPA was performed with total 40 ml 0.25% bupivacaine in the M group. Surgical infiltration was performed in the control group. The primary outcome of the study was the global quality of recovery score, the secondary outcomes were pain scores, rescue analgesic demands, and adverse effects during the 24-h postoperative period.
Results: The global quality of recovery scores at 24 h were significantly higher in the M group (p < 0.001). There was a reduction in the median static and dynamic NRS for the first postoperative 8 h in the M group compared to the control group (p < 0.001). The need for rescue analgesia was significantly lower in the M group compared to the control group (13 patients vs. 24 respectively, p < 0.001). The incidence of side effects was significantly higher in the control group (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: In our study, M-TAPA increased patient recovery scores, and provided pain relief in patients who underwent TAPP.
Register number: NCT05199922.
Keywords: Acute pain; Laparoscopic surgery; Pain management; Regional anesthesia; Ultrasonography.
Copyright © 2023 Sociedade Brasileira de Anestesiologia. Published by Elsevier España S.L.U. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest. This study had no funding.
Figures
References
-
- Elsharkawy H, El-Boghdadly K. Barrington M. Quadratus Lumborum Block: Anatomical Concepts, Mechanisms, and Techniques. Anesthesiology. 2019;130:322–335. - PubMed
-
- Tulgar S, Senturk O, Selvi O, et al. Perichondral approach for blockage of thoracoabdominal nerves: Anatomical basis and clinical experience in three cases. J Clin Anesth. 2019;54:8–10. - PubMed
-
- Tulgar S, Selvi O, Thomas DT, Deveci U, Özer Z. Modified thoracoabdominal nerves block through perichondrial approach (M-TAPA) provides effective analgesia in abdominal surgery and is a choice for opioid sparing anesthesia. J Clin Anesth. 2019;55:109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

