Heart failure pharmacological treatments and outcomes in heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction
- PMID: 37204037
- PMCID: PMC10509568
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvad036
Heart failure pharmacological treatments and outcomes in heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction
Abstract
Background: Guideline recommendations for the treatment of heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF) derive from small subgroups in post-hoc analyses of randomized trials.
Objectives: We investigated predictors of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors/angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitors (RASI/ARNI) and beta-blockers use, and the associations between these medications and mortality/morbidity in a large real-world cohort with HFmrEF.
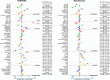
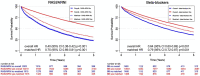
Methods and results: Patients with HFmrEF (EF 40-49%) from the Swedish HF Registry were included. The associations between medications and cardiovascular (CV) mortality/HF hospitalization (HFH), and all-cause mortality were assessed through Cox regressions in a 1:1 propensity score-matched cohort. A positive control analysis was performed in patients with EF < 40%, while a negative control outcome analysis had cancer-related hospitalization as endpoint. Of 12 421 patients with HFmrEF, 84% received RASI/ARNI and 88% beta-blockers. Shared-independent predictors of RASI/ARNI and beta-blockers use were younger age, being an outpatient, follow-up in specialty care, and hypertension. In the matched cohorts, use of both RASI/ARNI and beta-blocker use was separately associated with lower risk of CV mortality/HFH [hazard ratio (HR) = 0.90, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.83-0.98 and HR = 0.82, 95% CI: 0.74-0.90, respectively] and of all-cause mortality (HR = 0.75, 95% CI: 0.69-0.81 and HR = 0.79, 95% CI: 0.72-0.87, respectively). Results were consistent at the positive control analysis, and there were no associations between treatment use and the negative control outcome.
Conclusions: RASI/ARNI and beta-blockers were extensively used in this large real-world cohort with HFmrEF. Their use was safe since associated with lower mortality and morbidity. Our findings confirm the real-world evidence from previous post-hoc analyses of trials, and represent a further call for implementing guideline recommendations.
Keywords: Beta-blockers; Heart failure; Mildly reduced ejection fraction; Registry; Renin–angiotensin system inhibitors; SwedeHF.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures

References
-
- Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JGF, Coats AJS. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J 2016;37:2129–2200. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw128 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

